Abstract
The purpose of the study is to identity and develops a comprehensive construct for the entrepreneurs in Pakistani context. The study has used qualitative review to highlight the reasons of entrepreneurship and issues faced by emerging entrepreneurs in Pakistan. The study intended to investigate the extant literature on Entrepreneurial Opportunity Recognition. The researchers focused on reputed and leading journals in order to contribute in a more objective manner. A comprehend review indicates that not just entrepreneurial factors but also shows how setups are branded. The study also highlights a comprehensive psychological model for quantitative testing. The previous studies only shows the importance and factors of entrepreneurship, however, this study also have highlighted the reasons for branding in emerging entrepreneurship. The study will impact to elaborate clearly on the information's about not only entrepreneurship but also the directions towards branding.
Key Words
Entrepreneurship, Branding, Issues, Emerging, Pakistan
Introduction
In Pakistani society, people opt for the option of education solely for the purpose of employment, in order to survive in society. But this thought needs to be changed as entrepreneurship not only provides the opportunity of earning but also create employment to others. It also plays an important role in socioeconomic growth, resultantly adding to GDP uplift, the need of the hour for our economy as a developing country.
Besides it role in poverty alleviation, Entrepreneurship also has an enabling factor whereby individuals entire social circle and social class is transformed. It is for this reason that this research focused on the development of a strong psychological constructive model for men to opt the option of entrepreneurship, instead of looking for employment.
Despite an increased number of studies conducted over entrepreneurship, still there exists a clear gap in those studies our business schools' promote and prepare students for employment rather than entrepreneurship. According to the study of Bogan and Darity (2008) entrepreneurship need to replace by employment. So this research has a primary focus over a comprehensive model development and testing of the same model for entrepreneurship development in our societies.
This study has followed a descriptive method for the development of an entrepreneurship model. The study has focus why to entrepreneur and their better entrepreneurship presentation within society as well as the intentions to make it a strong brand in the future. According to the study of Sait and Semira (2016), there are three stimulating factors that affect entrepreneurial actions: the perceived approach of behavioral, control over behavior and the perceived social standards. So this mean that research will also take into consideration the religious factor for entrepreneurship almost the majority of the Prophets has opted entrepreneurship for survival in Khurshid (2017) society. How this religious factor would be a reason for entrepreneurship intention will be interesting to find?
The current economic conditions of Pakistan are under the threshold point where the cost of living is higher than income, in such circumstances moving towards entrepreneurship is becoming more important than going for employment. Because the entrepreneurs not only earn but also create employment opportunities as well. For this reason, quite frequently the government of Pakistan offers new schemes for young entrepreneurs in shape of interest free loan. Similarly, many business institutions in the country through their business incubations center are offering the same to students. Due to very same reasons this area has been choose for the research purpose to identify and develop a comprehensive model for men.
The ratio of men entrepreneurs is increasing in the world slowly and study on this topic is also educating and guiding men to this field. On their way, men are dealing with various cultural, economic, religious boundaries, more specifically; psychological issues are making their position in the market questionable. Developing nations like Pakistan needs to encourage men entrepreneurship and their contribution in the economy (Naseer and Shah 2020). As they are the major population contributor, so they can bring positive economic change (Colli & Guillen, 2013). Its awareness can lead to men empowerment and their contribution can give rise to the economy and can decrease the problems they are facing in absence of job contribution (Bagram and Khan, 2012). This topic has not yet well addressed by researchers so there is a challenge for researchers to look for the factors that are a challenge for men entrepreneurship and what can inspire men to shift to this concept and how young entrepreneurs not just start new business but also move it towards branding.
Weilerer (2001) and Misty (2003) stated that 27% of men are inspired either by hurdles they face in their growth or by the absence of challenges in their field. They plan to extend their business and face problems in it and got stuck (Misty, 2001; World bank, 2014). Some researchers also state that men are not facing any hurdles and they are being successful entrepreneur and are supported culturally and socially (Mehrang 2012). What can be the reasons that can motivate them to be an entrepreneur?
Men is the major contributor of the world population yet still not able to prove themselves as independent and successful entrepreneur because of social and global factors that internally and externally effects men behavior towards entrepreneurship. Only the West is paying attention to this alarming situation and trying to find its reasons (Reuben and Dunoma, 2018). The motivation for this study is the difference that exist between literature and my own interest in entrepreneurship; hence it is aimed as to find a fit and rationale Razavi, Abdolvahab, Esfandabadi, & Shahsavari (2014).
Methodology
Entrepreneurship is an international activity which is regularly developing worldwide. It has been observed that it has been researched in many parts of the world. Despite many studies has been conducted over entrepreneurship, but still there is a need for more theoretical and practical development in this area There is a need to investigate this area based on its importance, particularly the opportunity recognition construct in the entrepreneurship domain. The following diagram shows the phases of the study.
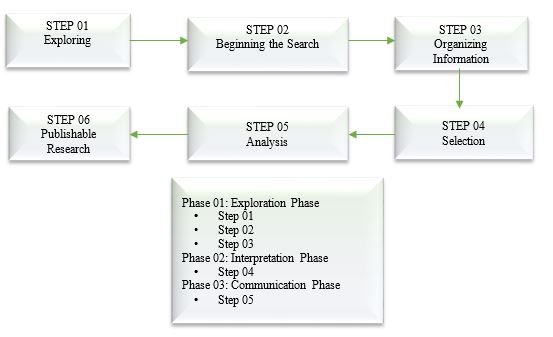
In order to further elaborate this study, he previous literature has been taken into consideration. Brief related literature of selected variables has been taken into consideration along with evidence based literature. The purpose was to have a comprehensive review which can represent and highlight the earlier work done in this area. The earlier literature has been taken into consideration and has been discussed in detail so the current study can be strengthened and elaborate in details on psychological factors.
The study has been discuss in three separate phases and uses a six-step approaches to move research from inquiry or research area selection through the generating publishable work. the first phase comprises investigation, which itself is constituent of four steps; examining the study topic; starting a search for certain constructs and variables; organizing storing the collected; and selecting and discarding data. The investigation stage was put up by scrutinizing the region and the research question. This was achieved by going through 250 research articles on Google Scholar. The research articles were further screened for their relevance with the study. The extended analysis articles shrined the number to around 120 articles that were considered most contributing to the current study. Where in Phase two researcher was engaged in developing logical interpretation and synthesis of earlier evidence-based data by identifying patterns which led to new frontiers. Phase three is organized as a communication phase; intended to lead into the whole study organized in a methodical manner to assist publication, and funding for other researchers and practitioners. Where phase three communicated the whole research in a structured form for a double-blind peer review.
Literature Review and Perceived Knowledge Gap
In this section, the researcher has tried to shed light on the extant literature and attribute the work of an eminent scholar of the field. Also, an effort is made to scrutinize the past literature and identify the potential research gap.
Self- enthusiasm
One of the most common factors in starting a business is self-enthusiasm, which means that either a person has a tendency towards business or he/she is looking for a Job? According to the study of Bharanti (2016) encouraging people for the business make them more enthusiast for startup of a new business. The study of Manaolova et al. (2008) describe in their study that there are three factors of entrepreneurship which are self-enthusiasm, investment for entrepreneurship, having an internal or external practically implemented idea. According to the study of Dianne (2017) it's the self-enthusiasm that compels a person for more innovation and creation in their businesses. The elf interest business has been observed more successful than those are being imposed. In order to understand the factor Kato (2013) shows that out 70% of business success rate is due to self-interest and motivation.
Social Personality
According to the study of Khurshid and Khokar (2021) personality traits are one of the important factor for business actions. She has discussed in her work in detail about it. She has also shown in her study that personality traits are directly link to entrepreneurship as one entrepreneur has to deal with personnel's and society. Therefore, it is much important to understand not only the personnel or the target market but also the society as a whole for initiating nay thing to that certain market.
The study of Watson (2013) has related the theory of planned behavior to communal or societal personality. In his study, he mentioned clearly the most of entrepreneurs start offering what they know, like what to offer, when to offer, to whom to offer, where to offer and the way to offer. He describes in his study that most entrepreneurs offer what their personalities are. The study has given examples of researchers, who started research firms; investigation officers who started investigating agencies etc. A personality trait is one of the common factor for initiating any new business setup.
According to the theory of social identity and the studies of (Tajfel and Turner, 1982), one always perform tasks that are aligned and present in their personality. Hence doing something with your personality traits and without the trait, will make a clear difference. Many other researchers have repeated the same phenomena in their studies. While communal personality develops in men as Asians are mostly male-dominant societies where the male is responsible for earnings as well as for the shared societal system. Therefore, more research is required to be conducted in this area. Hence this study is taking into consideration the factor of social personality and men's intentions towards new startups and entrepreneurship side development in Pakistan. The current studies are focusing over emerging entrepreneurs who emerged from a business institution as they have more information and ideas about current and new business trends.
Self- Respect
The living trend in the world is to earn and survive. Earning has simply two ways either to be an employee or either have your own earnings in the shape of a business. Self-respect to survive oneself is the ultimate goal. It not just allows a sense of accomplishment but also give self-confidence for further extensions (Abbasi and Sta 2019). According to the study of Ozlem (2014), self-respect is the key factor that shapes personality. Self-confidence is one of the most important factors for the success of new entrepreneurs. The earlier study has taken into consideration this factor and considered it one of the essential variables for studies.
Family Trend
The study of Pruett, Shinnar, Toney, Llopis, and Fox (2009) shows that family is one of the most reliable and supporting factor for entrepreneurship. In their study they have highlighted the three major role of the family which contributes towards entrepreneurship. The first is in terms of resources which can be either human resources or ether financial or can be both even. Second the family plays the role of valid and reliable information on which a person can take trust and third it also plays a role model source as well.
The study of Carley and Weibe (1989) shows that in the early stage of a business family play continuous support to entrepreneurs. Specifically, new business decisions with heavy investments are more complex hence in such circumstances the support of family is very important. It does not just make the decision quick and easy but it also reduce stress factors.
Many researches have taken into consideration the family support for entrepreneurship in different angels, like decision support, to become a business family together or being a human resource, the family tradition of business and family transformation towards entrepreneurship (Wang & Wong, 2004). There are two major key role that family plays for new startups, like new startup intentions for entrepreneurship so in such situations, the family also become the business team and the bond among relations become stronger. Secondly stress becomes common and solutions are identified on a mutual basis. The study of Sirmon & Hitt (2003) describe that family is an important stimulator for men entrepreneurship, as the new generation also inspired from successful businessman and follow the path in the future. Few psychological studies also have shown that the children of business oriented families are more creative than those of employees. Hence it can be concluded from the discussion that the role of the family cannot be denied in new business intentions and its play a very supportive role not only for startups but also for important decision making and future prolongers of businesses.
Gender Percipience
According to the study of Khan, Haider & Shah (2011), Asian countries are mostly male dominant and all the decisions and important financial decisions are made by males. Hence the role of male cannot be denied. Looking at the northern side of Pakistan, 99% entrepreneurs are male while the remaining areas are also based on male dominancy which is 92%. It means that the Pakistani market is based on male entrepreneurs. Hence the role of male cannot be ignored and this area need to be more polished.
The study of Zampetakis et al (2016) describe that being male is positively related to entrepreneurship intensions. As per the new reports of Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) that male entrepreneurship is 80% higher than female in Asian countries. The study of Kelley (2020) also mentioned that male entrepreneurs male has greater intension of entrepreneurship than any other gender. The third gender or transgender which are very less in number are also has been taken into consideration and it has been observed that they are also not good initiators for new startups and the reason is gender discrimination.
According to the study of Mueller and Dato-on, (2013), Asian men have greater motivation than those of Asian women for the return on investments, as well as business prolongers. This may be due to the fact that in Asian societies the responsibilities of families are all on male shoulders hence they have to produce and provide the maximum they cannot just in their personal lives but also in professional lives. According to the study of Khurshid (2021) that 52 % society of Pakistan is based males and 19% are entrepreneurs. The numbers is still low and there is a significant need to increase this ratio hence a complete comprehend model is required for male entrepreneurship.
Culture
The role of culture has been discussed by various researchers in their studies that it plays an important role in entrepreneurship. According to the study of Matondi (2013), culture openness play important role in a variety of business offering. He clearly mentioned in his study that various services offered are restricted in a different culture. Few cultures do not accept the kind of offering so the entrepreneurship intention of such services is being not imitated. The Islamic culture strongly supports the entrepreneurial concept. From start to end, almost all Holy Prophets have opted the business earning ideas. Hence it has been proved that cultural support plays an important role in the study of entrepreneurship and entrepreneurial intentions.
Self-Trust
Business startups need self-trust. The entrepreneur self-trust for the new business startup plays an important role. In other words, the self-efficacy of person is an essential element for driving a person towards entrepreneurship side. The study of Albert (2017) shows that men are stronger in comparison of women and hence this is the main reason that majority of the successful entrepreneur are males. Furthermore, the decision making specifically with the high investment are more commonly found in males.
Locus of Control
Different researchers and studies have defined this terminology but as simple as it can be defined as ''the belief of a person to have control over the result of an activity he or she performed''. The social environment of people plays an important role in the motivation of entrepreneurship intensions. Not just internal motivation as well as external motivation combine makes a significant impact over new business intentions. According to the study of Thurik & Dejardin (2012) a person's self-interest plays a positive significant role in the locus of control for the entrepreneurial intention as well as for further development of existing businesses. Hence the importance of locus of control cannot be denied in the studies of entrepreneurship and its related discussions.
The ability and confidence that a task can be completed or not is itself an important factor for consideration in new business startups. Most of the studies considered the locus of control in decision making and in psychological constructs. The physiologist studies describe that locus of control help a person to think in an innovative manner. According to the study of Brandsttter (2011), locus of control is one of the key factor for successful decision making but still very few and limited studies have linked entrepreneurship and locus of control and its implications.
Personality Trait
In today's dynamic world being a static personality no one can survive and compete until do not understand the updated requirements of currents markets. In order to understand the situational changes one own personality characteristics are essential side in order to be competitive. According to the study of Pretheeba (2014), variation in attitude towards entrepreneurship not only make it more competitive but also make it more customaries. The two same business operated by different persons create differences in their offering. Therefore, this study is taking into consideration the personality trait as in important variable to identify its role in the psychological construct.
This has been observed from the study of Brice (2004) where they have conducted a series of studies over entrepreneurs and haves concluded that entrepreneurs with fixed attitudes remain the same in their offering in comparison to those who have a positive variation in their attitude. Hence it has been becoming clear option that personality traits are influencing entrepreneurial intentions and entrepreneurial activities. Several other studies have emphasized over the importance of personality traits in decision making but in entrepreneurship, it's not only one factor that may contribute (Obschonka, Stuetzer, 2017). The business students comparatively have more detailed information about new venture start but still it has been observed very few of them start with their own offering. Is this because of personality traits? Such questions need to be answered in the area of this type of studies. This means the current studies are still lacking to describe and link the connectivity of personality traits and entrepreneurial intentions. The proper linkage of such a subjective factor needs to be evaluated and linked with entrepreneurship properly.
Earlier studies have taken only a few dimensions of personality like motivational factors and the reason is that these studies have taken only on open factors and not been conducted on two-dimensional factors like first to identify the entrepreneurial intention and secondly to find an appropriate measure of it. This is the reason that this factor has been taken into consideration and will be under the consideration not only for the psychological construct model for men entrepreneurship but also for practical testing and statistical experiments from entrepreneurs.
Individual Community
In surrounding every individual has their own circle of friends and fellows. What they are doing in their life and how they inspired you to do something is important to understand in the context of entrepreneurship. The Asian culture is mostly more based on a community based culture where support appears in the shape of not only friends but also in the shape of families. According to the study of Graham et al (2010) both family and non-family members are the basic individual social networks that leads a person toward the motivational side.
Many studies have been conducted on social networks motivation however few studies have identified its relationship with entrepreneurship. After studying deep literature of entrepreneurship the role of social networks cannot be denied as it's one of the most essential factors of motivation. According to the study of Krueger (1993) family social networks influence directly positive motivation for earnings and earnings intentions. Recent social sites compel people more towards social networking. The new era has created more entrepreneurship intensions in the shape of the service industry.
The study of Wiguna & Manzilati (2014) shows that the personnel networks of men are stronger than women, this is the reason that most of the men are entrepreneurs in comparison of men's. However how these social networks play the role of business intention yet need evaluation properly. The greater the size of the social network, the more ideas and intension may appear. The earlier psychology studies show that social networks influence motivation but however yet a gap is open to be filled to know how these networks influence entrepreneurial intension and entrepreneurial motivation. The concept of role models in the family and social circle is one of the key factors of motivation.
Spiritual Believes
Audretsch, Boente, and Tamvada (2013) describe in their studies that most of the entrepreneurial thought are dropped due to religiosity and spiritual believes. Peoples belong to different religions which make them intend differently to each business intention. So in every society, these beliefs take them various motivational levels for various entrepreneurship intentions. Therefore, as well as the economic impact of entrepreneurship it is also important to know the impact of the spiritual side and its impact of over entrepreneurship. The study of Henly (2016) shows that in every culture the importance of spiritual believe cannot be denied and their impact of daily based activities.
Theoretical Support of the Current Study
Planned Theory is the main theory of recent study that described lower along with slight other supporting theories.
The Theory of Planned Behavior
The idea of the planned theory is related to entrepreneurship and is concerned with the psychological structure associated with entrepreneurship. Human behavior is predicted and understood by many theories but the most popular theory is the theory of planned behavior (TPB) (Ajzen 1991) (Armitage and Conner 2001).
Entrepreneurial Intention
The very basic impression of business intention is the theory of Entrepreneurial Intention (Fay-olle & Linan, 2014; Malebana, 2014; Schlaegel & Koening, 2014 Krueger et al 2000). It can be said that there is a direct relationship between entrepreneurial intention and motivation Solesvik (2013). The most important intention for carrying some certificates is sole intention Ajzen (2015).
According to business intentions, behavioral attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control can be understood with greater accuracy (Ajzen, 2005, 2012; Ajzen & Sheik 2013). The interaction between TPB components and entrepreneurial motive has attracted substantial research (Solesvik et al, 2013), but the findings are still definitive. Researchers have identified a direct link between the three main TPB indicators and business intention (Tkachev and Kolvereid, 1999; Souitaris et al, 2007).
Attitude Towards Behavior
Behavioral attitude refers to individual favor or unfavorable evaluation of specific behavior. According to their beliefs, individuals change their attitudes and this thing affects behavior and attitudes (Ajzen, 2005). Attitude towards behavior in the business world refers to the difference between an individual's perception of aspiration to come and the need for self-employed employment (Souitaris et al. 2007).
Subjective Norms
Subjective standards refer to perceived social pressures to conduct the behavior or not to do so. To become an entrepreneur, social background gives an impression on both perceived attitude and behavior (Linan et al., 2013; Byabashaija & Katono, 2011).
Perceived Behavioral Control
Perceived control of conduct reflects the individuals, it also represents the ability and capability of the actions received. The drive to start a business is inspired by the awareness of men's business potential (Amoros & Bosma 2014). The perceived capacity has a greater effect on the motivation of the client to start a business than the perceived outcome (Townaend Busentz and Arthurs 2010).
Social Identity Theory
Tajfel (1978) stated that the concept of social identity had begun with work's social identification. (Turner et al, 1994) defined the philosophy of social identity emphasizes a human affiliation of different specific racial groups and reflecting on the causes and implications of recognition with a social group. Tajfel & Turner (1979) defined the theory of social identity theory which predicts some best as behaviors based on group differences in a perceived group state, validity, and stability of these differences. Ashforth and Fred Mael (1989) found that the person defines himself as part of the left group according to the theory of social identification. Perception of cohesion with a particular group or contributing directly or indirectly to a group that includes awareness of failure and success. Even without strong leadership or interdependence and interaction, group identification and selection tend to take place.
Identity Theory
We begin this work without expecting that identity can play a role in our theory and establish explanations of most of the experimental models mentioned until we understand the definition and adopt identity theory.. In a very general term Theory of Identity for a group of theories seeking to explain the human being's I or myself" in terms of the identity of individuals. When we talk about social psychology we rely upon the identity theory (Bruke & Stets, 2009) and social identity refers to psychological social psychology (Tajfel and Turner, 1979). There was a dispute between sociological and psychological interpretations of identity theory (see, for instance, Hogg, Terry, and White, 1995), and more recent work called for the inclusion of all views as compatible (Deaux and Martin, 2003). The closure of these two focal theories of phenomena in our study underlines the potential values of such integration.
Future Recommendations of the Study
The study can be tested quantitatively and the entrepreneurs can be checked and measured through a structured questionnaire to identify the real contributing factors towards entrepreneurship and branding. The study can also be checked with other sectors to identify some new reasons or factors which may contribute to entrepreneurial branding. The study can be also checked cross-sectional in quantities results with respect to different regions.
The researcher needs to figure out how a lack of resources can constrain proper research and how impeding work stress can cause mental distress. A bigger picture and the underlying dynamics may be shown by visualizing any variable across the three domains of the individual, organizational, and societal levels. Opportunity is closely related to each of these categories and has a significant influence on each one. Recognizing opportunities is essential for the entrepreneurial process for people. The same will apply to groups, such as business incubators and accelerators. Entrepreneurial activity will lead to increased economic activity, which will be advantageous to people, organizations, and society as a whole.
References
- Abbassi, R., & Sta, N. (2019). The Effect of self- esteem, entrepreneurship education, and entrepreneurial tradition of the family on the entrepreneurial intention among students. Journal of Business and Management Research, 12, 235-245.
- Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50, 179-211.
- Ajzen, I. (2005). Attitudes, personality and behavior (2nd ed.), Berkshire, England: Open University Press. Maidenhead: McGraw-Hill Education
- Ajzen, I. (2015). The theory of planned behaviour is alive and well, and not ready to retire: a commentary on Sniehotta, Presseau, and Araújo-Soares. Health psychology review, 9(2), 131-137
- Ajzen, I. 2012. The theory of planned behavior', In Lange, P.A.M., Kruglanski,A.W
- Altan-Olcay, Ö. (2014). Entrepreneurial subjectivities and gendered complexities: Neoliberal citizenship in Turkey. Feminist Economics, 20(4), 235-259.
- Ãlvarez, C., Urbano, D., & Amorós, J. E. (2014). GEM research: achievements and challenges. Small Business Economics, 42(3), 445-465.
- Armitage, C. J., & Conner, M. (2001). Efficacy of the theory of planned behaviour: A meta†analytic review. British journal of social psychology, 40 (4), 471-499.
- Ashforth, B. E., & Mael, F. (1989). Social identity theory and the organization. Academy of management review, 14(1), 20-39.
- Audretsch, D. B., Boente, W., & Tamvada, J. P. (2013). Religion, social class, and entrepreneurial choice. Journal of Business Venturing, 28(6), 774-789
- Bagram, M. M. M., & Khan, S. (2012). Attaining customer loyalty! The role of consumer attitude and consumer behavior. International review of management and business research, 1(1), 1- 12.
- Bharanti, B. E. (2016). Determinants of the entrepreneurial intention of papuan students (a study in Universities in Jayapura). Journal of Education and Vocational Research, 7(1), 41-47.
- Bogan, V., & Darity Jr, W. (2008). Culture and entrepreneurship? African American and immigrant self-employment in the United States. The Journal of Socio- Economics, 37(5), 1999-2019
- Brandstätter, H. (2011). Personality aspects of entrepreneurship: A look at five meta- analyses. Personality and individual differences, 51(3), 222-230.
- Brice, J. (2004). The role of personality dimensions on the formation of entrepreneurial intentions. In Annual Usasbe National Conference, 18, 1-9).
- Burke, P. J., & Stets, J. E. (2009). Identity theory. Oxford University Press.
- Byabashaija, W., & Katono, I. (2011). The impact of college entrepreneurial education on entrepreneurial attitudes and intention to start a business in Uganda. Journal of Developmental Entrepreneurship, 16(01), 127-144.
- Colli, A., GarcÃa-Canal, E., & Guillén, M. F. (2013). Family character and international entrepreneurship: A historical comparison of Italian and Spanish ‘new multinationals’. Business History, 55(1), 119-138.
- Deaux, K., & Martin, D. (2003). Interpersonal networks and social categories: Specifying levels of context in identity processes. Social psychology quarterly, 101-117.
- DINC, M. S., & Budic, S. (2016). The impact of personal attitude, subjective norm, and perceived behavioural control on entrepreneurial intentions of women. Eurasian Journal of Business and Economics, 9(17), 23-35.
- Graham, M. B., Landes, D. S., Mokyr, J., & Baumol, W. J. (2010). Entrepreneurship in the United States, 1920–2000 (pp. 401-442). Princeton University Press: Princeton.
- Gumbau Albert, M. (2017). Entrepreneurship, innovation and regional performance: Application for the Spanish regions. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 29(3-4), 271-291.
- Henley, A. (2016). Does Religion Influence Entrepreneurial Behavior? Journal of International Small Business , 1-21
- Hogg, M. A., Terry, D. J., & White, K. M. (1995). A tale of two theories: A critical comparisonof identity theory with social identity theory. Social psychology quarterly, 255-269.
- Hsieh, R. M., & Kelley, D. (2020). A study of key indicators of development for university- based entrepreneurship ecosystems in Taiwan. Entrepreneurship Research Journal, 10(2).
- Kato, S. (2013). Entrepreneurship as a process of self-fulfillment: well-being, affect, and behavioral strategies (Doctoral dissertation, Syracuse University).
- Khan, M. I., Shah, S. H. A., Haider, A., Aziz, S., & Kazmi, M. (2020). The Role of Supervisor Support on Work-Family Conflict and Employee Turnover Intentions in the Workplace with Mediating Effect of Affective Commitment in Twin Cities in the Banking Industry, Pakistan. International Review of Management and Marketing, 10(6), 42
- Khurshid, J., & Khan, M. I. (2017). Impact of self- efficacy on women entrepreneurial intention: mediating role of perceived behavior control and moderating role of openness to experience. J Manag Sci, XI (3), 276-291.
- Khurshid, J., Khurshid, N., & Khokhar, M. (2021). Impact of Psychological Factors on Women Entrepreneurial Intention: Mediating and Moderating Model. Indian Journal of Economics and Business, 20(4).
- Krueger Jr, N. F., Reilly, M. D., & Carsrud, A. L. (2000). Competing models of entrepreneurial intentions. Journal of business venturing, 15(5-6), 411-432.
Cite this article
-
APA : Khan, S., Ali, M. D., & Majid, A. (2023). Growing From Emerging Entrepreneurs into Brands: A Systematic In-depth Literature Review of the Psychological Factors. Global Social Sciences Review, VIII(I), 42-52. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2023(VIII-I).04
-
CHICAGO : Khan, Shahzad, Mohammad Daud Ali, and Abdul Majid. 2023. "Growing From Emerging Entrepreneurs into Brands: A Systematic In-depth Literature Review of the Psychological Factors." Global Social Sciences Review, VIII (I): 42-52 doi: 10.31703/gssr.2023(VIII-I).04
-
HARVARD : KHAN, S., ALI, M. D. & MAJID, A. 2023. Growing From Emerging Entrepreneurs into Brands: A Systematic In-depth Literature Review of the Psychological Factors. Global Social Sciences Review, VIII, 42-52.
-
MHRA : Khan, Shahzad, Mohammad Daud Ali, and Abdul Majid. 2023. "Growing From Emerging Entrepreneurs into Brands: A Systematic In-depth Literature Review of the Psychological Factors." Global Social Sciences Review, VIII: 42-52
-
MLA : Khan, Shahzad, Mohammad Daud Ali, and Abdul Majid. "Growing From Emerging Entrepreneurs into Brands: A Systematic In-depth Literature Review of the Psychological Factors." Global Social Sciences Review, VIII.I (2023): 42-52 Print.
-
OXFORD : Khan, Shahzad, Ali, Mohammad Daud, and Majid, Abdul (2023), "Growing From Emerging Entrepreneurs into Brands: A Systematic In-depth Literature Review of the Psychological Factors", Global Social Sciences Review, VIII (I), 42-52
-
TURABIAN : Khan, Shahzad, Mohammad Daud Ali, and Abdul Majid. "Growing From Emerging Entrepreneurs into Brands: A Systematic In-depth Literature Review of the Psychological Factors." Global Social Sciences Review VIII, no. I (2023): 42-52. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2023(VIII-I).04
