Abstract
Political polarization remains central to the political behavior scholarship. In this study, political polarization patterns among the youth of Pakistan with reference to selective exposure approaches of media were examined. Survey from 420 students of Pakistan public sector universities was conducted. It was found that selective exposure to media is still strong in Pakistan, however diverse exposure is also being witnessed in Pakistan. Now the people are also diverting towards diverse exposure. Consequently, political polarization among the university students of Pakistan is still strong. Findings imply that media in Pakistan is playing an important role in strengthening the democracy in Pakistan. Furthermore, it is also concluded that media played a key role to determine voters’ choice during Elections-2013 in Pakistan.
Key Words
Selective exposure, diverse exposure, political polarization, Pakistan elections-2013
Introduction
Methods
Cross-sectional
survey design was used as methodological design in this study. Population of
study was the university students of Pakistan. A sample of 420 subjects was
selected through cluster sampling technique. Five clusters of universities were
made on the basis of provinces; Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Balochistan,
and Islamabad capital territory. Data was collected from students of:
Quaid-e-Azam University, Islamabad; University of Gujrat, Punjab; Government
Collage University, Punjab; Punjab University, Punjab; University of Karachi,
Sindh; Behria University, Sindh; Peshawar University, KPK; and University of
Balochistan. Sample distribution presents in table 1.
Table
1. Sample
Distribution
|
|
Gender |
Total |
||
|
Female |
Male |
|||
|
Province |
Punjab |
56 |
64 |
120 |
|
Sindh |
75 |
36 |
111 |
|
|
KPK |
22 |
60 |
82 |
|
|
Baluchistan |
27 |
17 |
44 |
|
|
Islamabad |
44 |
21 |
65 |
|
|
Total |
224 |
198 |
422 |
|
Measures
of Study
Demographic
Information Sheet
Respondents
were asked questions about their demographic information, including; gender,
province and institutional affiliation.
Scale
for Media Exposure
Media
exposure was operationalized as the people consuming habits of media, including
electronic media, and online media. A 10-item scale was developed to measure
media exposure. Respondents opinion were measured at five-point Likert scale,
ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree. Items were about; watching
news bulletins, political discussions, political content, talk shows, watching
campaigns of political parties, use of social media for political information,
political discussion and vote casting awareness. Cronbach alpha reliability was
obtained 0.87.
Scale
for Selective Exposure
Selective
exposure was operationalized as the respondents’ tendency towards likeminded
media content. It was measure through 5-item scale. Responses were measured at
five-point Likert scale. Ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree.
Items were about; watching favorable information and supporting information
towards specific political party. Cronbach alpha reliability was 0.72.
Scale
for Diverse Exposure
Diverse
exposure was operationalized as the respondents’ tendency towards contradictory
media content to specific party. It was measure through 5-item scale. Responses
were measured at five point Likert scale. Ranging from strongly agree to
strongly disagree. Items were about; watching unfavorable information and
exposure towards information against respondent’s specific political party. Cronbach
alpha reliability was obtained 0.73.
Scale
for Political Polarization
Polarization
was operationalized as the respondents’ consistent attitude towards specific
political party. It was measured through 15-item scale. Responses were measured
at five point Likert scale. Ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree.
Items were about; strong political association, affiliation, blind following,
family party, rational analysis of party, defending political party, vote
casting to same party, less inclination towards other parties, persuading
others to specific party, and changing political affiliation. Cronbach alpha
reliability was obtained 0.78. For data analysis and results, we used
descriptive and inferential statistics by using SPSS version 20.
Findings and Discussion
The
present study found that educated youth of Pakistan has become very democratic
oriented in their media exposure (Table 2). Youth of Pakistan does not only
tend towards selective media messages, but also get themselves exposed to
diverse exposure (Table 2). In this way, it is argued that media in Pakistan is
promoting democratic values among university students. It is playing crucial
role in strengthening democracy in Pakistan. Hence H1a and H1b are supported.
It implies that Pakistani media has become pluralistic and it is promoting the
political messages of all the political parties in an effective way. People are
getting not only the like-minded messages but also the messages of the other
political parties.
Table
2. Descriptive
Statistics of Scales
|
|
N |
Range |
Min. |
Max. |
Mean |
SD |
|
Media Exposure Scale |
422 |
40 |
10 |
50 |
34.17 |
7.66 |
|
Political Polarization Scale |
422 |
49 |
21 |
70 |
42.22 |
8.75 |
|
Selective Exposure Scale |
422 |
20 |
5 |
25 |
15.58 |
4.06 |
|
Diverse Exposure Scale |
422 |
20 |
5 |
25 |
16.13 |
3.87 |
Further this study highlights
that selective as well as diverse exposure are high among university students
and they have become more polarized (Table 2). Political polarization among
university students correlates with selective exposure and diverse exposure
(Model 1). Therefore, regression analysis was executed to further validate the
best predictor of political polarization in university students. Results
indicate selective exposure as the best predictor of polarization, and diverse
exposure as the second predictor of polarization (Table 3, Model 1). In this
way, it is argued that media exposure in Pakistan has become selective and
partisan based. This selective mechanism is influencing polarization patterns
among youth. As it has been previously argued that selective exposure promotes
political polarization (Arceneaux et al., 2012; Fischer & Greitemeyer, 2010; Garrett, 2009; Iyengar et al., 2008; Messing & Westwood, 2012; Sears & Freedman, 1967; Stroud, 2008; Valentino et al., 2009). Hence, H2 is supported that
selective exposure of media is the best predictor of political polarization of
Pakistani youth.
Table
3. Predictor
of Political Polarization among the University students of Pakistan
|
Model Summaryb |
||||
|
Model |
R |
R Square |
Adjusted R Square |
Std.
Error of the Estimate |
|
1 |
.532a |
.283 |
.280 |
7.429 |
|
a. Predictors:
(Constant), Diverse Exposure Scale, Selective Exposure Scale |
||||
|
b. Dependent
Variable: Political Polarization Scale |
||||
|
Model |
Unstandardized
Coefficients |
Standardized
Coefficients |
T |
Sig. |
95.0%
Confidence Interval for B |
|||||
|
B |
Std.
Error |
Beta |
Lower
Bound |
Upper Bound |
||||||
|
(Constant) |
21.87 |
1.74 |
|
12.6 |
.00 |
18.458 |
25.296 |
|||
|
Selective
Exposure Scale |
.97 |
.100 |
.453 |
9.7 |
.00 |
.777 |
1.170 |
|||
|
Diverse Exposure
Scale |
.32 |
.105 |
.142 |
3.0 |
.00 |
.114 |
.527 |
|||
a. Dependent Variable: Political
Polarization Scale
However, findings also claim that media in Pakistan is not only reinforcing existing attitudes, but also providing opportunities towards diversity of views. Selective exposure and diverse exposure go side by side as it was found in previous studies (Conover et al., 2011; Gruzd, 2013; Valentino et al., 2009). This is a healthy indicator for working democracy in Pakistan.
Model 1
Relationship of Media Exposure, Diverse Exposure, Selective Exposure and Political Polarization among University students
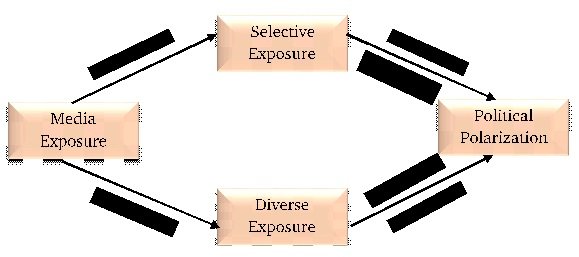
**
Significant at 0.01 level
* Significant at 0.05 level
Furthermore, study found that
significant gender differences exists in media exposure of respondents.
Independent sample t-test indicates that male respondents’ media exposure is
higher than female respondents (Table 4). It shows that women interest in political
news and their media consumption is still relatively low in Pakistan. Policy
makers must strive hard to bring equality in political participation of women.
In sum we can conclude that youth in
Pakistan is actively seeking political information not only relevant to their
predispositions, but also they are diverting towards diverse views and
opinions. Most of the youth is inclined towards selective messages of media,
which leads them towards strong polarization. On the other hand, youth is also inclined
towards diverse views on media which results in decline of polarization among
them.
Table 3. Gender Differences in
Democratic Orientation, Media Exposure, Selective Exposure, Diverse Exposure
and Political Polarization among the University students.
|
|
Levene's Test for Equality of
Variances |
t-test for Equality of Means |
||||
|
F |
Sig |
t |
df |
Tow Tailed Sig |
||
|
Media Exposure Scale |
2.230 |
.136 |
-4.135 |
420 |
.000 |
|
|
|
|
-4.098 |
391.381 |
.000 |
||
|
Political Polarization Scale |
1.638 |
.201 |
-.717 |
420 |
.474 |
|
|
|
|
-.714 |
403.470 |
.476 |
||
|
Selective Exposure Scale |
1.891 |
.170 |
-.937 |
420 |
.349 |
|
|
|
|
-.928 |
389.417 |
.354 |
||
|
Diverse Exposure Scale |
.586 |
.445 |
-1.396 |
420 |
.164 |
|
|
|
|
-1.398 |
416.207 |
.163 |
||
Conclusion
The present study strongly argues that media exposure is bringing awareness in the society of Pakistan. The findings of the study state that diversity of media landscape have changed the prior trends of selective exposure and people go for contradictory arguments which increase their knowledge. There not only is an acceptance of the views which reinforce the public’s beliefs, but counter attacks on political parties are also acceptable. Electronic and social media expose all kinds of investigative reports and it seems attractive. Youth of Pakistan tends to expose themselves to all kinds of news to get diverse knowledge. Education, media and emerging political parties have changed the concept of politics in Pakistan. In the political system of Pakistan, the trend of right wing and left wing allies have been demolished and a good debate within right and left wing has been started on performance and ideology. The mentality of the youth of Pakistan has been changed. With the presence of sound and moderate public opinion, a healthy democracy emerges.
References
- Arceneaux, K., Johnson, M., & Murphy, C. (2012). Polarized political communication, oppositional media hostility, and selective exposure. The Journal of Politics, 74(01), 174-186.
- Baldassarri, D., & Bearman, P. (2007). Dynamics of political polarization. American sociological review, 72(5), 784- 811.
- Bernhardt, D., Krasa, S., & Polborn, M. (2008). Political polarization and the electoral effects of media bias. Journal of Public Economics, 92(5), 1092-1104.
- Campante, F. R., & Hojman, D. A. (2013). Media and polarization: Evidence from the introduction of broadcast TV in the United States. Journal of Public Economics, 100, 79-92.
- Conover, M., Ratkiewicz, J., Francisco, M., Gonçalves, B., Menczer, F., & Flammini, A. (2011). Political Polarization on Twitter. Paper presented at the ICWSM.
- Dilliplane, S. (2014). Activation, conversion, or reinforcement? The impact of partisan news exposure on vote choice. American Journal of Political Science, 58(1), 79-94.
- Feldman, L. (2011). Partisan differences in opinionated news perceptions: A test of the hostile media effect. Political Behavior, 33(3), 407-432.
- Fischer, P., & Greitemeyer, T. (2010). A New Look at Selective-Exposure Effects An Integrative Model. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 19(6), 384-389.
- Garrett, R. K. (2009). Politically motivated reinforcement seeking: Reframing the selective exposure debate. Journal of Communication, 59(4), 676-699.
- Garrett, R. K., Gvirsman, S. D., Johnson, B. K., Tsfati, Y., Neo, R., & Dal, A. (2014). Implications of Proâ€and Counter attitudinal Information Exposure for Affective Polarization. Human Communication Research, 40(3), 309-332.
- Groseclose, T., & Milyo, J. (2005). A measure of media bias. The Quarterly Journal of Economics, 1191-1237.
- Gruzd, A. (2013). Examining Polarization in Political Social Media: A Case of Twitter and the 2011 Canadian Federal Election. Paper presented at the Proceedings of the Annual Conference of CAIS/Actes du congrès annuel de l'ACSI.
Cite this article
-
APA : Bilal, M. Z., Ali, A., & Ullah, S. (2019). Effects of Media Exposure on the Political Polarization Patterns of Students in Pakistan. Global Social Sciences Review, IV(III), 292-298. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-III).38
-
CHICAGO : Bilal, Muhammad Zahid, Arshad Ali, and Sami Ullah. 2019. "Effects of Media Exposure on the Political Polarization Patterns of Students in Pakistan." Global Social Sciences Review, IV (III): 292-298 doi: 10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-III).38
-
HARVARD : BILAL, M. Z., ALI, A. & ULLAH, S. 2019. Effects of Media Exposure on the Political Polarization Patterns of Students in Pakistan. Global Social Sciences Review, IV, 292-298.
-
MHRA : Bilal, Muhammad Zahid, Arshad Ali, and Sami Ullah. 2019. "Effects of Media Exposure on the Political Polarization Patterns of Students in Pakistan." Global Social Sciences Review, IV: 292-298
-
MLA : Bilal, Muhammad Zahid, Arshad Ali, and Sami Ullah. "Effects of Media Exposure on the Political Polarization Patterns of Students in Pakistan." Global Social Sciences Review, IV.III (2019): 292-298 Print.
-
OXFORD : Bilal, Muhammad Zahid, Ali, Arshad, and Ullah, Sami (2019), "Effects of Media Exposure on the Political Polarization Patterns of Students in Pakistan", Global Social Sciences Review, IV (III), 292-298
-
TURABIAN : Bilal, Muhammad Zahid, Arshad Ali, and Sami Ullah. "Effects of Media Exposure on the Political Polarization Patterns of Students in Pakistan." Global Social Sciences Review IV, no. III (2019): 292-298. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-III).38
