Abstract
Computer-Mediated Communication (CMC) have brought about a new medium for information sharing and communication and weblogs are becoming more and more popular in the virtual sphere. The process of code-switching can be traced in this fast evolving medium of communication. This paper aims at investigating the existence of code-switching patterns by examining the categories and frequency of Urdu code-switches in Pakistani English weblogs authored by Pakistani bloggers. The quantitative and qualitative approaches were used in this study. The blog entries of 10 Pakistani bloggers were analyzed by using the descriptive research paradigm. The findings illustrated that the linguistic choices of Pakistani bloggers as bilingual internet users are living in between two worlds, two cultures, and two languages which they employ in this mode of communication to fully express themselves. The findings showed the linguistic features that are particular to the context of CMC. The study concluded that the presence of code-switching in CMC have to be considered and treated as a unique and different entity from spoken form or written form of code-switching to capture its fundamental attributes.
Key Words
Bilinguals, Code-Switching, Computer-Mediated Communication, Pakistani English Weblogs, Pakistani Bloggers, Weblog
Introduction
Language is an essential aspect of daily life as it is the primary means of communication for human beings. It is used to share and provide information to other individuals. People can choose from a wide variety of languages for their communication in various contexts. It is vital to choose one legal language for correspondence in order to avoid misunderstandings. People must select a certain language and decide whether to switch or not from one to another. The process of code-switching refers to the switching between two languages. According to Rathert (2012, p.7), one method of communicating linguistic identity is through code-switching. It is considered as “a valuable strategy of bilinguals in making linguistic choices for communicative purposes”.
All aspects of modern life are rapidly transitioning to digital form due to the quick improvements in technology and the ubiquitous usage of the Internet. Computer-Mediated Communication (CMC) is one of the communicative contexts where language is extensively studied and offers a vibrant and wider setting for linguistic and sociolinguistics studies.
Language plays a substantial role in intercultural exchange of ideas, the preservation of cultural legacy, social development, high-quality education, and the establishment of one's own identity. Therefore, the competence of speaker being able to speak a language other than the native tongue of the speaker provides several benefits. The ability to converse in two or more languages is a trait of multilingual or bilingual individuals. The bilingual or multilingual speakers have several advantages, such as benefits for cognitive growth, better learning, communication, culture, and work.
The language contact and policy are considered to be the main reasons of code-switching from one language to another. Gumperz (1982) provided the definition of code-switching process as the "juxtaposition of the same linguistic transaction." The use of multiple languages by the speaker in a single conversational event is referred to as this practice in linguistics. Therefore, the language of developing Computer-Mediated Communication can be linked to the linguistic change caused by the phenomena of code-switching.
According to Crystal (2001), Internet is presently changing from being a homogeneous linguistic medium to a collection of diverse dialects. Due to the rapid nature of message transmission, the use code-switching technique in face-to-face encounters may transfer to social media communication. Hu, Talamadupula, & Kambhampati (2013) stated that the internet users frequently use the abbreviations and compressed word spellings in order to accelerate the message encoding on social media, even if the communication medium is written as the text is typed in digital form. Emoticons, capitalization, and punctuation are employed in place of nonverbal cues, which are common in face-to-face communication. Crystal (2006) proposed that the revolution in language has occurred with the adoption of emoticons in Netspeak.
Nowadays, people are frequently connecting and communicating with others via online mode. This process is recognized as Computer-Mediated Communication (CMC). In 2006, David Crystal created this terminology to classify and categorize the various forms of online communication. Weblogs are quite novel type of CMC and its usage by the users on the World Wide Web is growing with the passage of time. A definition of blog was provided by Crystal (2006) in his work as an illustration of “online diaries or frequently modified web pages that are arranged in a reverse chronological sequence”. Herring (2004) believed that “weblogs are the latest genre of Internet communication that are gaining widespread popularity with the passage of time”.
The current article attempts to look into the existence of code-switches in Computer-Mediated Communication, specifically in English weblogs maintained by Pakistani bloggers. The objective of the current study is to examine the instances of Urdu code-switches in English weblogs.
Significance of the Current Research
The results of this research study reveal patterns of code-switching in online textual communication. This information contributes in the comprehension of code-switching phenomenon in the Pakistani blogosphere. This study is substantial as bilinguals and multilinguals will be aware of the code-switching phenomena that occurs during virtual communication through various social networking platforms, such as weblogs. The findings are fruitful for language educators and decision makers as they are motivated and ready for pursuing language change by utilizing the data of online modes of communication.
Research Objective
The research objective of this study is;
1. To investigate the linguistic data of Pakistani English weblogs and examine the patterns of code-switching identified in Pakistani English weblogs authored by Pakistani bloggers.
Research Questions
In this research paper, the following research questions are addressed:
1. Do Pakistani bloggers freely switch languages in Pakistani English weblogs?
2. What are the patterns of code-switching found in English weblogs authored by Pakistani bloggers?
3. Which type of code-switching is most commonly employed by Pakistani bloggers in English weblogs?
Literature Review
Code-Switching: A Process to Linguistic Maintenance of Language Contact
Hoffman (1996, p.110) has defined the process of code-switching as “the alternate use of two languages or linguistic varieties within the same utterance or during the same conversation”. It is the normal attitude of individuals to frequently switch between different language codes in a single multilingual situation. A code is a spoken or written communication system, similar to a language, dialect, or variant, in sociolinguistics. Wardhaugh (1986, p. 103) suggested that “people then are usually required to select from one code to another or to mix code”. It means that the linguistic switching takes place frequently and in a variety of ways.
Corder (1981) further explained this notion in a more traditional way that the phenomena of code-switching in a communicative process is still thought to be a random activity, however interference may provide a better explanation. It is one of the rule-governed communication techniques used by internet users today. According to Zentella (1981), when a language user switches between two languages during a conversational event, the process of code-switching happens.
Computer-Mediated Communication (CMC) as a Novel Linguistic Genre
Computers and other technological devices are used in this type of communication. According to Higgins (1991), CMC can be defined as "human communication via computer". The existence of Computer-Mediated Communication has been made possible by a wide range of contemporary technology and networking services. It enables inter-personal communication through the usage of computing machines and other digital/electronic gadgets and networks. It consists of social networking websites such as electronic mail, Instagram, bulletin boards, weblogs, facebook and video conferencing etc. Additionally, it also includes the network communication in chat rooms through instant messaging.
Social media websites are under the public or semi-public domain of online communities. People can build profiles in this online space and submit relevant information either publicly or privately. Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, Snapchat, Tik Tok, Twitter, weblogs, and other similar platforms are examples of social networking websites. Surprisingly, there is no comparison between the conversation that takes place on these networking websites and other forms of communication. The online information on social media is distinct in nature as it is available in the form of forum posts or comments. It may be viewed by all forum members and in certain networks, even the users who are not members of that particular forum can view the data. It consequently belongs to the category of "public domain".
Code-Switching process in Computer-Mediated Communication
The emergence of Computer-Mediated Communication (CMC) is not a novel concept as mentioned by Crystal (2006, p. 2) The Internet has been a part of global media since 1960 and it incorporates the features from earlier communicative mediums like the telephone or television. A study conducted by Goldberg (2009, p. 4) examined the instances of code-switching in emails sent to five contributors from the region of Latin America in both Spanish and English language. The results indicated that speakers mostly used the English language for work-related activities or for aspects of their professional lives. However, the native languages were used for a variety of everyday activities. The use of code-switching in oral or written communication is a linguistic phenomenon that has already been the focus of numerous research projects. The process of code-switching in the textual form of Computer-Mediated Communication in the Pakistani blogosphere has not yet been investigated, more particularly in social networking websites that have only lately become popular.
Weblogs
A Web-related communication tool that is now gaining popularity is blogging. Blogs will soon be a major source of information and the future media influence. The basic components of online blogs involve text, images, videos, and connections to pertinent online pages and media. Blog readers can interact with authors of the blog by leaving comments.
Weblogs, also known as blogs, are one of the prevalent and popular forms of online communication. Blogs are described as constantly updated web pages with material that are arranged in reverse chronological order. Stauffer (2002, p. 15) has provided the definition of weblogs or blogs as a form of website that displays the features similar to personal journals. It is developed in a systematic way and easy to manage. The content of the blog updates in a linear way based on the date and time of publication. Tim Berners-Lee developed the first website in 1991 and the first blog was initially published at that time. The modern format debuted in 1996 and the name "weblog" was first used to refer to it in 1997. The terms "blog" (an online diary), "blogger" (someone who owns and maintains a blog), and "blogging" are all used in the blogging community (the action of creating for the blog).
Figure 1
Standard Format of Weblog
Languages Spoken in Pakistan and the Phenomena of Bilingualism
The lineages of bilingualism process in Pakistan may be traced in the eighteenth century, during the governing period of British raj in the sub-continent. The British colonial rule introduced the concept of authority and language in the subcontinent. According to Kachru (1986), Colonization is a significant component for driving the bilingualism forward. In Pakistan, the speakers may combine several dialects or linguistic types in their regular conversation, deliberately and subconsciously. Sometimes they keep switch between languages in their chat and they also try to combine few words from other languages to get and deliver the desired message in order to achieve the aim of communication.
Pakistan has a population of about 182.1 million and it is a bilingual and multicultural nation (World Bank, US Census Bureau 2013). Almost 7.5% of Pakistani speakers in the country use Urdu as their first language. The utility of Urdu language in a conversation is extremely important in order to exhibit the national identity and harmony. On the other hand, it is commonly acknowledged that English is considered as the de facto lingua franca. It is established as a global means of communication.
In this background, the idea of globalized world has significantly affected the multilingual setting of Pakistan. In Pakistan, English has therefore become a significant component of the semantic distinction. The usage of linguistic processes such as code-mixing, code-switching, and borrowing of English language to regional and national languages are some indicators of rising status of English has grown in Pakistan. Due to the fact that Pakistan is a multilingual nation, code-switching is a prevalent process in Pakistan.
According to Mehmood S. and Taswir T. (2013), more than 80 provincial languages are spoken in Pakistan. Urdu and English are considered to be the ‘majority’ languages in Pakistan because they have high status and utility in the country. These languages are used by the powerful institutions for official tasks and educational purposes. The language policy has traditionally favored these two languages over regional languages, which are the native language or mother tongue of majority of Pakistani speakers.
The investigation of code-switching in Pakistan begins with the concept of bilingualism. Language change has reportedly been a continuous process in Pakistan as mentioned by Yousaf (2004). A child born in Pakistan initially learns his native or regional language at home and becomes accustomed to Urdu language through his environment while residing in Pakistan. As he grows older, he must learn English for scholastic and professional purposes. English is now a significant component of our daily life conversation.
The Linguistic Practices of Computer-Mediated Communication in Pakistan
The rise of the Internet as a communication and informational tool in Pakistan is a tale of remarkable, occasionally controversial transformation in this traditional environment of the country. Pakistani nation has always been struggled with access to information and freedom of speech. It is still learning the value the freedom and discovering the online forum to engage and communicate recently.
Talaat (2005) suggested that in addition to being a language phenomenon, code-switching also serves the social functions and it leads to the phenomenal language change. The use of print and digital media in Pakistan are making reference to this language transition. Since Pakistan is a multilingual nation, the process of code-switching is also visible in the online environment of Pakistan. He suggested that the use of online communication is substantial in the promotion of social communicative practices that include code-switching. It symbolizes the growth of verbal conduct of multilingual communities.
Linguistic and Sociolinguistic Approaches to Code-switching
Bilingual speakers may express themselves in several languages. Bilinguals frequently switch between the two languages when speaking with other bilinguals. The two main areas of code-switching research are linguistic or grammatical and sociolinguistic or pragmatic aspect.
The research study conducted by Blom and Gumperz is considered as a revolutionary and influential work produced from this perspective in 1972. They described the practice of code-switching as "situational code-switching" and "metaphorical code-switching" and established a categorization for it. Situational code-switching is described as an alteration in the social context that is brought on by the speaker's reciprocal obligations. The change of topic is used to cause metaphorical code-switching, which alters the identities or roles of the speakers.
According to the linguistic approach, there are various types of code-switching. The three main forms of code-switching were described by Poplack (1980). It includes intra-sentential code-switching, inter-sentential code-switching, and tag switches (the usage of an exclamation point or tag phrase). He suggested that the process of code-switching demonstrates the ability of the speaker to communicate effectively in two languages.
The Markedness model, introduced by Myers-Scotton in 1993, showed that the code-switching process may be utilized to identify the speaker’s identity in various social circumstances. It offers an explanation for the social indexical driving force behind the code-switching. Myers-Scotton (1993, p.50-51) suggested that the process of “Code-switching at this point was considered only a ‘skilled performance’ by bilinguals rather than a legitimate subject”. After analyzing the available data on code-switching, he claimed that the linguistic decisions made by Africans can be classified as "marked" or "unmarked."
An influential concept known as the Matrix language frame model was also put out by Myers-Scotton in (1993). The terms "matrix language" and "embedded language" refer to the languages used for code-switching. The morphological and syntactic structure of the code-switched text is established by the matrix language, which serves as the base language and it attempts to provide the system morphemes. Code-switching phenomena is comprehended as "the selection by bilinguals or multilinguals of forms from an embedded variety (or varieties) in utterances of a matrix variety during the same conversation" (p.3).
Theoretical Framework of this Study
The process of code-switching happens in Pakistani blogosphere due to the presence of multilingual communities in Pakistan. The theoretical background offered by Montes-Alcala (2000 & 2007) with reference to the categorization of code-switching was utilized for this study. Additionally, it was complemented by the notions of Appel and Muysken (1987 & 2005). The following categories of code-switching were utilized in this research study:
1. Lexical Switches
2. Switches for Quotations
3. Tag Switches
4. Switches for Emphasis
5. Switches for Elaboration
6. Triggered Switches
However, the findings of the present study revealed that the occurrence of a single switch served multiple socio-pragmatic purposes simultaneously. Conversely, there was overlapping in the utility of the switches that were part of the study
Research Methodology
The qualitative and quantitative approaches were utilized in the current
investigation. In order to provide a fair picture of Urdu code-switching with
reference to its socio-pragmatic functions in Pakistani English weblogs, this
research study combines both qualitative and quantitative data. Johnson &
Turner (2003,
p.299) proposed that the data available in
quantitative and qualitative form have been merged in order to accomplish the
"complementary strengths and non-overlapping flaws". Bentham (2007)
stated that the paradigm of quantitative research indicates “the systematic
empirical investigation of certain social phenomena via the use of statistical,
mathematical or numerical data or computational techniques”. According to Nunan
(1998), it would be a study in which the researcher applied the quantitative
approach in one phase and the qualitative approach in the following phase. In
this paper, the weblogs were used to extract quantitative data in the form of
frequency counts of classified categories and the switches were subjectively
examined.
The descriptive content analysis was used as the best method for
qualitatively analyzing the text in the form of categories of code-switches
identified in Pakistani weblogs to offer the satisfactory answers to the
research questions. Nunan (1998) proposed that the
purpose of using descriptive methods in research is to provide a brief summary
of the situation or characteristics of the phenomenon. The categories of
code-switching utilized for Pakistani English weblogs were located, measured,
and described by using the content analysis. In this study, the categories were
manually coded and the frequency count or occurrence of each code-switch was determined
and then the descriptive analysis was made.
Population and
Sample
The participants of this study were Pakistani bloggers who maintained
the posts on English weblogs. The population of Pakistani bloggers served as
the sample of the current study. The English weblogs authored by Pakistani
bloggers were initially examined to gather the information about the
availability of code-switches.
Weblogs were chosen for the current study because
they provide a wide range of examples of how language is used in written form
of online communication. This cutting-edge kind of Computer-Mediated
Communication is considered as an amalgamation of spoken and written language.
The corpus of blogs was constructed by choosing
English blogs from online weblog directories, such as Pakistani blogs,
WordPress, Urdu point, etc., and other publicly accessible blog search engines.
Each sample of blog post was authored by a single author. Table 1 provides the
details of sample of the current study. Table 2 offers the profile information
of Pakistani bloggers:
Table 1: English Weblogs & Pakistani
bloggers
|
S. No |
Blogs and Bloggers |
Nos. |
|
1. |
Pakistani
English Weblogs |
10 |
|
2. |
English
Blogs written by Pakistani Male bloggers |
05 |
|
3. |
English
Blogs written by Pakistani Female bloggers |
05 |
Table 2: Profile of Pakistani Bloggers
|
Bloggers |
Gender |
Location |
Switch From |
|
Blogger
1 |
Male |
Pakistan |
English
to Urdu |
|
Blogger
2 |
Male |
Pakistan |
English
to Urdu |
|
Blogger
3 |
Male |
Pakistan |
English
to Urdu |
|
Blogger
4 |
Male |
Pakistan |
English
to Urdu |
|
Blogger
5 |
Male |
Pakistan |
English
to Urdu |
|
Blogger
6 |
Female |
Pakistan |
English
to Urdu |
|
Blogger
7 |
Female |
Pakistan |
English
to Urdu |
|
Blogger
8 |
Female |
Pakistan |
English
to Urdu |
|
Blogger
9 |
Female |
Pakistan |
English
to Urdu |
|
Blogger
10 |
Female |
Pakistan |
English
to Urdu |
The sampling method of the present study is Probability sample as the
sample blogs were chosen by using the simple random sampling method. Two blog
posts of each blogger were selected for the study. The sum of 20 blog posts
written by male and female Pakistani bloggers were examined in this study.
The blog entries were read manually and the
instances of Urdu code-switches were examined to discover the code-switching
process in English blogs. In order to determine the kind of code-switches found
in the blog entries, an additional analysis was done.
The data representation of code-switches was done
by using frequency counts, tables and bar charts. In order to avoid any
ambiguity, the corpus of weblogs was taken in its original form for analysis
with all of its imperfections, including misspelt words in the text, improperly
formed sentences, incorrect grammatical structure, the use of linguistic or
nonlinguistic symbols, etc.
The personal blogs were taken into account for
analysis of the data in this study. The data of the bloggers was acquired
through the open display of their profile information, which includes their
demographic information. The Pakistani bloggers of middle and young age groups
were involved in this study with at least educational qualification of
intermediate level. The theme or topic of the sample blogs were based on
various subjects.
Mostly bloggers choose to make
all of their personal details available to the public on their profiles.
Herring et al. (2004) identified that the home page of blogs makes their personal
information publicly visible. The findings of the present study showed that roughly 80% of Pakistani
bloggers revealed their real names on blog. Furthermore, it was noted that the
majority of Pakistani bloggers had prominently displayed the data regarding
their personal information such as their name, label of blog, age, gender, and
place of residence on the home page of their weblogs.
Most bloggers choose to make all of their personal
details available to the public on their profiles. Herring et al. (2004) identified that the home page of blogs makes their
personal information publicly visible.
Research Procedure
A
thorough action plan for data analysis was used for this study. In the initial
stage of this study, the data was extracted from English language blog entries
posted by male and female Pakistani bloggers. In the 2nd step, the
analysis was conducted to identify the code-switches at lexical and
sentence/phrasal level. In order to analyze the frequency of code-switches, the
current study is built on the theoretical background offered by Montes-Alcala (2000 & 2007). In the last step, the switches extracted from the online textual discourse
were analyzed.
Data
Collection Process and Representation
The sample size for the current research study was 05
Pakistani male bloggers and 05 Pakistani female bloggers. Two blog entries with
an average word count of 800 words were chosen randomly from each blog of all
the bloggers. Each sample of blog entry had an average word count of 400 words.
If the blog entries were written between the time span of January 2017
-December 2021, they were considered to be eligible for the analysis.
Various techniques were utilized
to search the relevant weblogs, including utilizing search engines to identify
the relevant blog by using keywords like "Pakistani English Weblogs"
and browsing other accessible blog rolls of Pakistani bloggers, online weblog
directories and linkages on other social networks. In this study, it was also possible to identify the
bloggers from Pakistan based on the subjects and themes of their blog posts. It
was consequently necessary to carefully read through the blog postings.
This study opted for the quantification approach, which
includes calculating the frequency of code-switches occurring in the data in
order to contextualize and examine the linguistic data of the transcripts. The
quantity of code-switches occurred in the blog post was calculated by using the
frequency count. The average and percentage of these switches were also
calculated. Tables and bar charts were used to represent the data of the
research study.
Ethical Considerations
Holmes (2009) proposed that the material uploaded or posted on blogs, pages, stories, social media walls, chartrooms, and boards is often accessible to the public. The information that is available online can be viewed for years. When a blogger is no longer active on social media or cannot be reached after a considerable amount of time and efforts, it might be a challenging task to trace them. In such kind of situations, it is assumed that these blogs are considered to be accurate and act as a reliable source of data for research studies, much like newspaper or letter archives.
Data Analysis of the Study
Montes-Alcalá (2000 & 2007)
observed the bilingual articles to examine the code-switching procedure in
bilingual journals. She discovered that the private diaries like weblogs have
bulk of the features typical of oral code-switching literature. Therefore, the
findings of her studies display that public journals such as blogs also exhibit
the socio-pragmatic functions. The classification used in this study was based
on the categories provided by Montes-Alcalá (2000 & 2007). The frequency and percentage of Urdu switches found in Pakistani
English weblogs for each category are listed in Tables 3.
Table 3: Category-wise Frequency and Percentage
of Switches Found in Pakistani English Weblogs
|
S. No |
Category |
Male Bloggers |
Female Bloggers |
Number of Switches in Pakistani English Blogs |
Percentage of Switches |
|
1 |
Lexical Switches |
145 |
101 |
246 |
3.07 |
|
2 |
Switches
for Quotations |
15 |
7 |
22 |
0.27% |
|
3 |
Tag Switches |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0.01% |
|
4 |
Switches for Emphasis |
21 |
23 |
44 |
0.55% |
|
5 |
Switches for Elaboration |
16 |
7 |
23 |
0.28% |
|
6 |
Triggered Switches |
14 |
20 |
34 |
0.42% |
Table
4 provides the snapshot of the number of code-switches found in per blog
authored by male blogger for each category.
Table 4: Number of Switches per Blog in
Pakistani English Weblogs Authored by Male Bloggers
|
S.
No
S.No |
Categories
employed by Male bloggers in Pakistani English weblogs |
Blogger
M-1 |
Blogger
M-2 |
Blogger
M-3 |
Blogger
M-4 |
Blogger
M-5 |
Total |
|||||
|
Blog
Post A |
Blog Post B |
Blog Post A |
Blog Post B |
Blog Post A |
Blog Post B |
Blog Post A |
Blog Post B |
Blog Post A |
Blog Post B |
|||
|
1 |
Lexical Switches |
12 |
28 |
23 |
23 |
2 |
3 |
24 |
14 |
2 |
14 |
145 |
|
2 |
Switches for Quotations |
4 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
15 |
|
3 |
Tag Switches |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
4 |
Switches for Emphasis |
4 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
6 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
21 |
|
5 |
Switches for Elaboration |
7 |
5 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
16 |
|
6 |
Triggered Switches |
5 |
0 |
6 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
14 |
Table
5 provides the snapshot of the number of code-switches present in per blog
authored by female blogger for each category:
Table 5: Number of switches per blog in
Pakistani English Weblogs authored by Female bloggers
|
S. No |
Categories employed by Female bloggers in
Pakistani English weblogs |
Blogger F-1 |
Blogger F-2 |
Blogger F-3 |
Blogger F-4 |
Blogger F-5 |
Total |
|||||
|
Blog Post X |
Blog Post Y |
Blog Post X |
Blog Post Y |
Blog Post X |
Blog Post Y |
Blog Post X |
Blog Post Y |
Blog Post X
|
Blog Post Y |
|||
|
1 |
Lexical Switches |
5 |
11 |
0 |
4 |
11 |
10 |
24 |
22 |
5 |
9 |
101 |
|
2 |
Switches
for Quotations |
1 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
7 |
|
3 |
Tag Switches |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
4 |
Switches for Emphasis |
2 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
8 |
3 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
23 |
|
5 |
Switches for Elaboration |
1 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
7 |
|
6 |
Triggered Switches |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
11 |
3 |
0 |
4 |
20 |
It
is evident that the distribution of code-switches is not uniform across all
Pakistani weblogs nor even inside a single blog. In this study, the bloggers
used tag switches very rarely i.e. once on average, but they switch at higher
frequency for other categories, including lexical items and switches for
emphatic reason. There is variation in the percentage of switches of different
categories.
Findings and Discussion
Lexical Switches
There is a lack of precise translation of certain expressions in the matrix language. The phrase "lexical switches" describes terms or noun phrases that are substituted because of biculturalism as opposed to lack of proficiency. Lipski (2005, p. 13) has investigated the use of English lexical unit "so" in Spanish sentences in order to differentiate between code-switching and borrowing. Additionally, Lipski offered the fundamental standards for separating code-switching from borrowing. This distinction states that lexical borrowing is a conscious and repeated choice that is purposeful and deliberate. In such situations, the word's origin is frequently lost and the monolingual speakers start using it in a natural way. In code-switching, on the contrary, the switches are produced either consciously or subconsciously by the bilingual speakers during communicating with the other bilingual speakers.
Languages are considered open and words are frequently borrowed by languages from others and such expressions never retained their original form. Such expressions go under significant phonological, morphological, and semantic modifications. The process of hybridization is evident in this study as the majority of these modifications are undertaken with consideration of regional flavor.
This category was the most productive of all as 3.07% of lexical switches in Urdu language were found in Pakistani English weblogs. It has been referred to as "lexical need". Since, every lexical switch in the data of this study almost fulfils a need. However, this should never be understood as a lack of linguistic competency, but somewhat as the deficiency of an equivalent counterpart in the other language. The further elucidation could be a momentary linguistic gap in the vocabulary of the speaker. It could be due to the more frequent exposure of a specific linguistic term in the base language. Additionally, the switching of lexical items (singular nouns and noun phrases) is more related to the element of biculturalism of the speakers instead of a lack of ability in any of the languages used. The words in this corpus are culturally bound to the Urdu world.
In this corpus, various instances of switches for kinship/family terms and phrases or food items are found in Pakistani English weblogs, such as in examples below;
i. You think you are the one following your chachu ki pardosan ki ajeeb si cousin….
ii. Rooh Afza is practically a Ramzan institution
in Pakistan but the bright red sherbet is full of sugar and colorings.
iii. One gentlemen whose khattay aalo has right amount of spice mix.
iv. The manzar at the border is similar on both sides.
v. Thank you Ammi, for raising me the way I'd want to raise my daughter.
Figure 2
Frequency of Lexical Switches used by Male and Female bloggers in Pakistani English Weblogs

Switches for Quotations
The direct citation of the user’s speech and the citation of speech of other speakers are done by code-switching. It may be inferred that the shift between two separate codes for quoting speeches are employed to maintain the legitimacy of the message. The category of quotations suggested by Montes-Alcalá (2007, p.167) includes those switches that take place to directly and indirectly cite someone else's remarks. The researcher discovered that only 0.27% of the switches of this category were found in the corpus of Pakistani English weblogs.
i. 'Aurat-ki-qismat-ka-inhesar-uskay-husn-e-surat,-husn-e-seerat,-taleem,-samajhdari-ya-mohabbat-par-nahien-bal–k-uski-zindagee-mein-shamil-honay-walay-mard-per-hota-hai'
ii. "Larkey, kia teray walidain Dilli ya Lucknow say hein?"
iii. “Nahin! Allah Mian kehtay hein so jao!”
iv. He says “aap kal subah aain”.
Figure 3
Frequency of Switches for Quotations used by Male and Female Bloggers in Pakistani English Weblogs.

Tag Switches
The insertion of a tag in one language to an entirely foreign language speech is the fundamental idea behind tag-switching. It mostly occurs in bilingual utterances. It can be introduced in a number of positions inside an utterance without disrupting the syntactic structure. Kanakri and Ionescu (2010) defined this category as a tag is a specific set of words from one language which are combined with terms from another language in code-switching process.
In this case, the tag switches were considered as the least productive category with only 0.01% found in Pakistani English weblogs. The example of tag switch is given below;
i. Kia faraq parta hay anyway... Parta hai kia?
Figure 4
Frequency of Tag Switches used by Male and Female Bloggers in Pakistani English Weblogs

Switches for Emphasis
If someone wishes to express themselves emphatically during a dialogue, the user will use a language that would not be the first or native language of the user. According to Hoffman (1991), this is a planned or unintentional transition from a second language to a primary language. McClure (1981) also demonstrated that the act of code-switching can be utilized as a tool to emphasize the concepts during oral interactions.
A lexical item, phrase or sentence can be brought to the reader's attention by underlining or capitalizing the text. In addition to these commonly accepted practices, a bilingual person also has the choice to emphasize something in his writing by utilizing both languages. Emphasis can be produced with either a simple code-switch or repetition in code-switched language. This form of code-switching was also among those that occurred most frequently in the data.
The data of Pakistani English weblogs contained almost 0.55% of emphatic switches such as;
i. WARNAAAA
ii. Aaj Janay Ki Zid Na Karo!
iii. Larkay!
iv. Ramadan as fasting.
v. ….giving rations/groceries to those who can’t afford them……
Figure 5
Frequency of Emphatic Switches used by Male and Female Bloggers in Pakistani English Weblogs

Switches for Elaboration
According to Zentella (1997), the switching between languages to further elaborate, clarify, or explain what has already been expressed is another common pragmatic phenomena frequently observed in multilingual communication. This kind of switching is achieved by embedding the equivalent word, phrase or sentence available in other language within the text. Due to the placement of switched lexical word, phrase, or sentence within parentheses or commas, these linguistic expressions frequently appear as a parenthetical comment.
Following are some instances where a concept is developed or clarified through the use of code-switching. The switched word, phrase or sentence may occasionally be placed in parentheses or between dashes to exhibit the elaboration. In the
below mentioned examples, the addition of switched words and phrases (in the other language) along with the content in base language is presented in parenthesis and even without parenthesis as well. In any event, each of these examples primarily serves to develop a concept without impairing the readability of the phrase in the base language. The data of Pakistani English weblogs contained almost 0.28% of elaborative switches such as;
i. Dahi (Yoghurt)
ii. Formal register Urdu (zab?n-i Urd?yi mu?allá ??? ????? ???? ? ?????)
iii. Each drummer marked an area in whose streets he played a large drum (dhol).
iv. They collected cash gifts (Eidy) from those whom they had dutifully roused for thirty consecutive early mornings.
v. During the month of fasting (Ramadan) ……..
Figure 6
Frequency of Elaborative Switches used by Male and Female Bloggers in Pakistani English Weblogs

Triggered Switches
The spoken language has regularly witnessed this remarkable phenomena as Valdés-Fallis (1976) proposed that the process of code-switching occurs when an unintentional word change causes what follows before or behind it to change (in the case of anticipatory triggering). The occurrence of a triggered switch due to a single lexical transition is a common practice.
This category was also productive with existence of 0.42% of triggered switches in Pakistani English weblogs. It has been noted in the literature that the occasional switching of word or expression may result in a switching of what appears after or prior to it. The examples of triggered switches found in Pakistani English weblogs are as follow;
i. Rooh Afza is practically a Ramzan institution in Pakistan but the bright red sherbet is full of sugar and colorings.
ii. Qawwali is perhaps the most popular ritual but communal dhikr.
iii. On Eid day, they arrived wearing patent khaki uniform and upon receiving cash Eidy …..
Figure 7
Frequency of Triggered Switches used by Male and Female Bloggers in Pakistani English Blogs

Code-switching is a process of expressing the cultures in addition to
the languages. Zentella (1997, p.114) suggested that the process of
code-switching is basically “a way of saying that they belonged to both worlds,
and should not be forced to give up one for the other”. The findings mentioned
in table 6 and 7 of this paper revealed that the category of lexical switches
was the most productive of all with the highest frequency of switches in
Pakistani English weblogs. However, tag switches were considered as the least
productive linguistic switch in Pakistani English weblogs due to its minimal
occurrence in blog entries.
Table 6: Overall Number of Code-switches Utilized
by Male and Female Bloggers in Pakistani English Weblogs
|
S.
No |
Categories |
Total Number of Switches in Pakistani English Weblogs |
|
1 |
Lexical Switches |
246 |
|
2 |
Switches
for Quotations |
22 |
|
3 |
Tag Switches |
1 |
|
4 |
Switches for Emphasis |
44 |
|
5 |
Switches for Elaboration |
23 |
|
6 |
Triggered Switches |
34 |
Table 7: Frequency
Distribution of Code-switching Categories in Pakistani English Weblogs
|
S.
No |
Class Intervals |
Number of Code-Switching Categories |
|
1 |
1-35 |
4 |
|
2 |
36-70 |
1 |
|
3 |
71-106 |
0 |
|
4 |
107-142 |
0 |
|
5 |
143-178 |
0 |
|
6 |
179-214 |
0 |
|
7 |
215-250 |
1 |
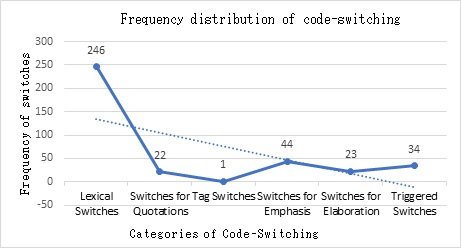
There is a difference of 35 points between class intervals. The below
figure demonstrates the distribution of the frequency scores for the categories
of code-switching that is not normally distributed. The categories of
code-switching falls within the 07 class intervals i.e. between the values of
1-250 according to the number of switches per category. The highest frequency
of code-switching category in Pakistani English weblogs is 246 for lexical
switches and the lowest frequency is 1 for tag switch. A line graph is used to
depict the aforementioned distribution.
Figure 8
Graphic Representation of Frequency Distribution of Code-switching

Conclusion
In Pakistan, code-switching is a common practice, especially among educated young people who are using the social media platforms frequently today. This process has been identified in blogosphere of Pakistan, specifically in Pakistani English weblogs as blogs provide a rich data for linguistic analysis. Although the process of multilingualism in Pakistan have been a topic of study for a number of linguistic scholars in spoken and written text, but there has never been a detailed study conducted on Pakistani weblogs with reference to the code-switching process. This study aids in highlighting the code-switching practice used by Pakistani Internet users in the medium of blogging. As the current study aimed at analyzing English weblogs authored by Pakistani bloggers, it leads to surfacing the few evident conclusions. The findings of this study revealed that when bloggers are writing in this mode of public journals, they switch codes/languages. It serves as an answer to the research questions of this study. The practice of code-switching has frequently been associated with the social stigma in verbal communication. It has been noted that this stigma does not appear to apply to informal written expression, particularly in a democratic communicative forums like Internet. Since, the frequency of code-switching in Computer-Mediated Communication occurred at lower rate in this study as compared to the face to face interaction or written mode.
Secondly, Herring (2001) quoted that the blurring of the lines between spoken form and written form of language in the context of Computer-Mediated Communication is one of its most remarkable characteristics. As a result, the textual communication in the contexts of Computer-Mediated Communication, especially in synchronous communication, shares the majority of the characteristics produced in face-to-face interactions. In this study, it was found that Pakistani bloggers made utilization of all the categories of code-switches. The category of lexical switches was the most productive one and tag switches were the least productive category in the data. Danet & Herring (2007) proposed that although most of the internet communication is in written form, the language is considered as less accurate, less complicated, and less coherent than standard written language. These features of internet communication bring the process of code-switching closer to it similar to the spoken language. According to Crystal (2001), the textual content created in synchronous communication of Computer-Mediated Communicative situations exhibit many colloquial aspects of verbal language, including constructions in shorter form, use of citations, lexical and phrasal repetition, use of tags, solidarity, and the usage of reaction signals (you know, okay, you see). According to him, language is simplified by the real-time users to accomplish the objective of interactive communication in this medium. The blogs of this study also contained these features in order to enhance the meaning of the text available on weblogs.
Thus, weblog code-switching is somewhat comparable to spoken form of code-switching in terms of linguistic exhibition and deliberateness, but its discourse functions highlight the characteristics unique to Computer-Mediated Communication contexts. The linguistic choices of Pakistani bloggers revealed that the bilingual internet users are living in between two worlds, two cultures, and two languages which they employ in this mode of communication to fully express themselves. Despite the fact, the code-switching process in Pakistani English weblogs is mostly an extension of spoken or written language. The conclusion showed the linguistics features that are particular to the context of CMC. In this regard, it is concluded that code-switching in Computer-Mediated Communication has to be treated as a separate unit from spoken form or written form of code-switching in order to fully understand its intrinsic characteristics.
Recommendations and Future Works
Computer-Mediated Communication is a subject that has not been fully explored so far from all directions; on the contrary, it has only just begun. The rise of the Internet and its usage in our daily lives have led to an expansion of Computer-Mediated Communication. According to Crystal (2006, p.259), the future of Computer-Mediated Communication will connect the means of communication together even more, such as vision and sound. This study is only an initial attempt to investigate the phenomena of code-switching in Pakistani English weblogs. To paint a more accurate picture of this phenomenon in Pakistani blogosphere, further studies involving larger and diverse research sets would be required. Additionally, comparative studies for the use of switched languages across a variety of different genres of Computer-Mediated Communication should also be looked into.
Moreover, there is a lack of research studies on code-switching in the numerous online platforms with a wide variety of languages, which gauges the linguistic diversity online. A comprehensive study can be conducted on the interactive form of Computer-Mediated Communication with reference to the code-switching phenomena.
Note: This Research Paper is a Part of PhD Dissertation
References
- Appel, R., & Muysken, P. (2006). Language Contact and Bilingualism. Amsterdam: University Press.
- Baker, A. (1998). Cyberspace couples finding romance online then meeting for the first time in real life. CMC Magazine. World Wide Web:
- Blood, R. (2000). Weblogs: A history and perspective. Rebecca’s pocket.
- Norway, I., Gumperz, J., & Hymes, D. (Eds.), Directions in sociolinguistics. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
- Crystal, D. (2001). Language and the Internet. Cambridge: University Press.
- Corder, S. P. (1981). Error Analysis and Inter language. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Danet, B., & Herring, S. (2007). The multilingual Internet: Language, culture, and communication Online. USA: Oxford University Press.
- Goldberg, R. N. (2009). Spanish English code- switching in Email communication. Language at Internet. 6(3), 1-21.
- Gumperz, J. (1982). Conversational Code- Switching. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge U Press.
- Herring, S. C. (1999). The Rhetorical Dynamics of Gender Harassment On-Line. The Information Society, 15(3), 151–167.
- Herring, S. C. (2004). Computer-mediated discourse analysis: An approach to researching online behavior. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Herring, S. C. (2001). Computer-mediated discourse. In D. Schiffrin, D. Tannen, & H.Hamilton(Eds.), The Handbook of Discourse Analysis (612-634). Oxford: Blackwell Publishers.
- Hoffman, C. (1991). An Introduction to Bilingualism. New York: Longman.
- Holmes, J. (2001). An Introduction to Sociolinguistics. Edinburgh: Pearson Education.
- Hu, Y., Talamadupula, K., & Kambhampati, S. (2021). Dude, srsly?: The Surprisingly Formal Nature of Twitter’s Language. Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, 7(1), 244-253.
Cite this article
-
APA : Fatima, K., & Qadir, S. A. (2022). A Tale of Two Languages in Blogging: Code-Switching Analysis in Pakistani Blogosphere. Global Social Sciences Review, VII(IV), 64-81. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2022(VII-IV).08
-
CHICAGO : Fatima, Kanwal, and Samina Amin Qadir. 2022. "A Tale of Two Languages in Blogging: Code-Switching Analysis in Pakistani Blogosphere." Global Social Sciences Review, VII (IV): 64-81 doi: 10.31703/gssr.2022(VII-IV).08
-
HARVARD : FATIMA, K. & QADIR, S. A. 2022. A Tale of Two Languages in Blogging: Code-Switching Analysis in Pakistani Blogosphere. Global Social Sciences Review, VII, 64-81.
-
MHRA : Fatima, Kanwal, and Samina Amin Qadir. 2022. "A Tale of Two Languages in Blogging: Code-Switching Analysis in Pakistani Blogosphere." Global Social Sciences Review, VII: 64-81
-
MLA : Fatima, Kanwal, and Samina Amin Qadir. "A Tale of Two Languages in Blogging: Code-Switching Analysis in Pakistani Blogosphere." Global Social Sciences Review, VII.IV (2022): 64-81 Print.
-
OXFORD : Fatima, Kanwal and Qadir, Samina Amin (2022), "A Tale of Two Languages in Blogging: Code-Switching Analysis in Pakistani Blogosphere", Global Social Sciences Review, VII (IV), 64-81
-
TURABIAN : Fatima, Kanwal, and Samina Amin Qadir. "A Tale of Two Languages in Blogging: Code-Switching Analysis in Pakistani Blogosphere." Global Social Sciences Review VII, no. IV (2022): 64-81. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2022(VII-IV).08
