Abstract
The most convenient and important part of the public transportation system is that provided by public buses, the most practical and cost-effective type of public transportation system. An expert system alone cannot accurately locate a bus stop. The "Natural Movement" theory of Space Syntax provides a deep understanding of "centrality" and urban activity, predicting the city's most dynamic streets and areas that serve as centres of urban activity. This study analyzed the city of Mansehra, Pakistan to provide a scientific evidence-based approach to planning of efficient transportation system. To find the best routes and bus stops, we computed centrality through spatial analysis and urban activity index, and vehicular and pedestrian traffic volume indices. The results of this research highlighted areas that are considered optimal traffic routes, busy city streets, and city centres, and represent the best locations for bus stop spacing in the city.
Key Words
Space Syntax, Spatial Analysis, Bus Stops Optimization, Spatial Attributes, Mansehra City, Public Transportation
Introduction
Due to the growing urban population, Pakistan is facing major traffic problems. The rapid growth of cities and high population densities have increased the demand for transportation. From 1 million in 1990 to 6 million vehicles in 2019, the exponential growth is alarming (Pakistan Bureau of Statistics, 2019). In addition, traffic congestion, vehicle pollution and traffic fatalities are the most common problems in the country's major cities. To deal with these disruptions, public transportation systems can play an important role and provide city planners with competent solutions. The primary purpose of urban transit systems is to provide convenience and support to commuters. It not only provides prospects for passenger and freight transport but also influences the development pattern and level of activity of the urban environment in the long run, based on the accessibility it provides (Hansen, 1959). Improving urban transport systems is therefore an important issue for city planners and designers, and improved distances between bus stops can effectively increase the efficiency of public transport systems.
Literature Review
Due to the rapid urbanization and population increase, as well as the rise in private car ownership, urban transport networks need to be supported by law. Bus stops are acknowledged as the primary meeting spot between passengers and buses in the majority of locations where the bus-related transit system serves as the primary mode of public transportation. The most comprehensive coverage is provided by public bus services in a crowded urban environment. Because it may be difficult to ensure door-to-door accessibility for every passenger with a disability. In transportation policy, urban buses are essential to reaching this social goal. Transit services centred on buses are the main form of transportation in Pakistan and many other developing nations. Because thoughtful bus stop layout will increase the demand for public transit users, reduce the use of private vehicles and traffic congestion, and enhance urban life.
In large cities, promoting bus-related public transit would assist to lessen the impact that transportation-related problems have on the environment. According to Nalawade et al. (2016), public transit will significantly contribute to improving the prestige of metropolitan life and boosting urban attractiveness. It is normal to go from one area to another, and using a vehicle is the best option.
By offering a variety of activities, essential services, and valued connections, geography and social economy have a significant impact on spatial relationships (Rodrigue, 2020). The urban transport system is greatly aided by public bus service, which also has positive social and economic effects. Public buses utilise fewer resources than private automobiles when running the amount of money invested, the number of passengers, the number of private automobiles on the road, and the bus service.
If there were fewer cars on the road, most problems with the public transport system could be resolved and traffic would be less congested.
Additionally, public transportation emits less carbon than private vehicles because it may accommodate up to 20 to 30 passengers every boarding.
According to the discussion in the study's opening lines, public bus transit plays a significant part in the network of urban transportation. The position of bus stops can be optimised to increase the bus system's efficacy. Urban planners must carefully consider public demand, an acceptable walking distance, and the least number of bus stops necessary to provide the best service coverage when choosing the site of bus stops (Xuebin, 2010).
According to Farewell, the maximum distance to walk to the bus stop is 400 meters, since people favour smaller walking distances to longer transit times. The public transport system would become more appealing by cutting down on the amount of time needed to go to the bus stop (Farwell & Marx, 1996). Fletterman (2008) assessed two objectives of bus stop placement models, to decrease the overall distance that passengers must travel to get to the bus stop, first. Second, there should be a minimum number of bus stops across the whole bus-based system. The distance, journey duration, and required access to the bus stop from that location were all taken into consideration. The bus-based system may be improved, in accordance with Murray's study, by enhancing trip comfort, applying effective pricing, reducing travel time, improving accessibility to bus terminals, and offering more convenient service (Murray, 2001). The effectiveness of routes and service coverage were addressed via bus-based management and planning (Murray, 2003). The main goals of the ideal bus stop position are to maximize coverage, serve the largest possible population, and minimize operating expenses (Guihaire, & Hao, 2008). To cut down on car travel time, a public bus-based transportation system needs to be designed so that commuters may get to their destination promptly. According to Bertonlini & Spit (1998), any "significant station" should be located in a notable area in an urban zone. According to Bertonlini and Spit (1998), a "significant station" in this context is a place that is likely to be accessible. However, certain urban network locations offer significant potential for migration. Based on space syntax analysis, many models and indicators of an urban environment might be used to gauge spatial accessibility. According to Texas Transportation Institute and Texas A&M Research Foundation (1996), the implementation of the transportation system and the degree of user satisfaction are significantly impacted by stop spacing, the design, operational service, accessibility, and location of the bus stop.
Figure 1
Natural Movement
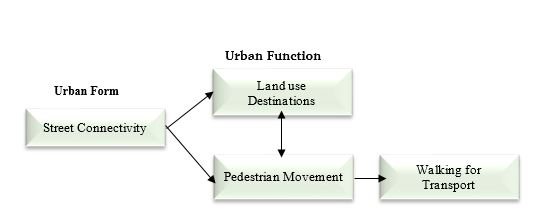
Bus stop spacing and proper planning may significantly raise the calibre of a public transportation system (Alterkawi, 2006). Customer demand, travel duration, accessibility, and speed may all have an impact on where the bus stop should be located (Chien & Qin, 2004). Therefore, maintaining appropriate walking that satisfies public demand and covering the necessary service area with a minimal number of stops is the main goal of the best bus stop position. Many studies have used space syntax analysis for pedestrian movement, and the results have produced an aggregated selection of consistent patterns. Peponis also utilized a real study of Atlanta, Georgia, in the US to show how space syntax may be used to analyze pedestrian mobility (Peponis, Ross, & Rashid, 1997). This approach was also used by Hillier to determine the distribution of urban crime rates. He associated the syntactic indices with crime rates, and the results indicated that the connectedness of a region was inversely correlated with the crime rate (Hillier & Shu, 2000). Spatial syntax theory suggests that street networks in urban layouts are formed by both natural patterns and urban activity patterns/organizations perceived as a single connected spatial system. Components such as road network analysis, correlations, and associated spaces extrapolated from the map form a single continuous spatial system (Hillier, 1999). The spatial syntax is a comprehensive methodology and scientific method for analyzing, evaluating and designing architectural and urban spatial configurations. It is commonly used in both new developments and existing urban environments. It measures urban and architectural spatial systems in terms of their composition. Constituent system integration, selection, connectivity, and strength results help identify potential routes and stop across networks in urban environments. The spatial syntax is a method for describing and analyzing the relationship between the social and spatial structures of urban networks. Hillier suggested that the use of graphic illustrations is one of the main techniques in spatial analysis using spatial syntax. For example, using a chart on an axis map creates different types of edges and vertices. These diagrams represent roads as vertices that represent relationships between roads (Hiller, 2005).
Consolidation indicates how many turns must be made in the network. Predict pedestrian road use and cognitive complexity to reach the road. This means that the more integrated roads are, the easier they are to access and the more they are used (Teklenburg, Timmermans & Van Wagenberg, 1993). To summarize Bill Hillier's words, the spatial accessibility of a city network is greatly influenced by its level of integration. Bus stops within an integrated area are therefore more likely to influence the natural movement of pedestrians and improve the efficiency of public transport systems.
Based on extensive expertise in accurately locating bus stops, most research has been done to optimize bus stop spacing. Ammons (2014) researched various bus stop standards around the world and found that typical bus stop spacing he found to be between 200 and 600 meters. Furthermore, Riley states that due to differences in traffic regulations, the distance between bus stops in Europe varies between 330 meters and 550 meters (Reilly, 1997). Sankar et al. (2003) and El-Shair (2003) used the well-known Geographic Information System 'GIS' for their research. As a primary method for determining bus stop spacing, 80% of residential and commercial areas are considered bus stop locations.
In order to appropriately use the findings, prior researchers sought to overcome the issue of the average distance between bus stops. There are several optimization objectives, including reducing travel time for consumers, increasing income for service providers, and lowering expenses for manufacturers and suppliers of products and services.
Chen argued that the spatial-syntactic approach differs from other techniques and methods because it uses land parcels as the unit of analysis. Enström & Netzell (2008) argued that conventional gravitational theory only considers movement from one place to another. Turner (2007) argued that spatial centrality, as opposed to point-to-point connectivity, is a better predictor of human locomotion behaviour.
A case study from the Mansehra Municipality in Pakistan's Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province's Hazara Division served as the basis for this study. The city acts as a middle point of entry into northern Pakistan. It has an estimated population of 1,556,460, of whom around 49% are men and 51% are women, according to the 2017 census. The city is equipped with commercial, educational, medical and administrative services and serves as a major centre for all surrounding villages and suburbs.
Three main arteries of the city in the sense of primary roads, secondary roads and territory roads. The main routes within the city are the Karakorum Highway, the N35 and the Mansehra Bypass Road. Secondary roads include Kashmir Road, Safida Road, Shinkyari Road, Danguri Road, Abbottabad Road and some other routes connecting the road settlements. Smaller routes that connect secondary roads and act as branch lines for main and secondary roads have been considered the three main roads of the city of Mansehra.
Methodology
Spatial syntactic techniques were employed as a key tool to identify the most integrated and best-connected route. Spatial data were collected in the form of base maps, roads, and road networks to begin spatial analysis of the city of Mansehra. Base maps were digitized using AutoCAD software. The spatial structure of the road network was analyzed by creating axial maps using UCL's depth map software. Axial analysis was performed on local and global scales. The global level results helped identify likely roads/routes and the local level results helped plan the optimal bus stop locations. The goal-counting technique was also used for field observation. In this context, the results of the spatial analysis were superimposed with manual field observations to validate the process. These values were used to generate scatterplots using both spatial analysis and field observations of 10 gated counts at peak hours.
Research Framework
Axial map Analysis
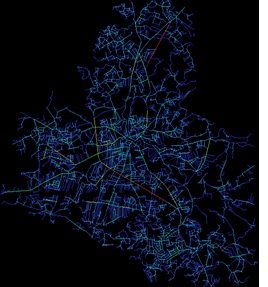
For axial map analysis, depth map software was used to create axial maps of the study area. Before creating the axial map, we used tracing techniques to convert the existing Google format to AutoCAD format. After running the analysis, the depth map displayed numerical values and a heat map showing the range of colours from red to blue to visualize the data. Red indicates high uptake values and blue indicates low uptake values.
Figure 2
Axial map of Mansehra city Source: Author
Segment Map Analysis
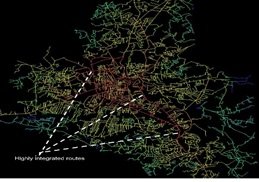
The second phase involved doing segment map analysis, a decision-making procedure that offers guidance and many options for transportation planning. The study was carried out at various radii from short, medium, and long distances, accounting for bicycle, pedestrian, and vehicle movement at short, medium, and long distances.
In this study, the following radius considering pedestrian accessibility to the bus stop was considered. The 400-meter range or 5-minute walking distance was used for pedestrians. 800 meter range was used for 10 minute walking distance and 1200 meter range was used for 15 minute walking distance.
Figure 3
Segment Map of Mansehra in Global Integration (radius N)
Gate Count/Field Observation
The field observations used in this study used the Gate Count Technique Spatial Syntax Laboratory developed by University College London (UCL). The viewer perceives the imaginary line on the street as a gate and perceives the flow of pedestrians and vehicles passing through the gate. In this study for detailed field observation, we marked 10 gates at different locations in the study area as gates and observed pedestrian and vehicle flow patterns. The field survey he carried out during peak hours from 1:00 pm to 3:00 pm as shown in figure 3.
Figure 4
Gate Count for 10 gates of the study area. Source: Author

Urban Activity Index is used to estimate the most efficient routes for cities on a worldwide scale utilising NACH (Normalised Angular Choice) values, which give more reliable data than raw values. In segment map analysis at the global level, the NACH value was calculated using the formula below. According to the theory of space syntax, the busy streets with high pedestrian/vehicular volume and activity are indicated by NACH values in segment map analysis that ranges from 1.3 to 1.6.
Figure 5
Normalize angular choice analysis Source: Author
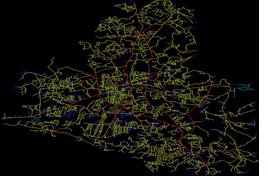
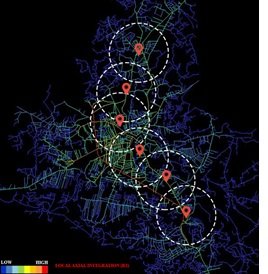
The centrality index was determined by angle integral measurements. r=5 means that 5 step/angle curves should be created in the road network. Local-scale maps highlight areas as central/sub-central areas with the highest centrality index suggestive of pedestrian-accessible bus stops. This measurement allows us to classify centres and sub-centres within an area based on the resulting measurement. This indicates that this metric can be used to plan the optimal location of major terminals and minor bus stops and to identify optimal routes within city networks.
Figure 6
Optimal location of bus stop Source: Author
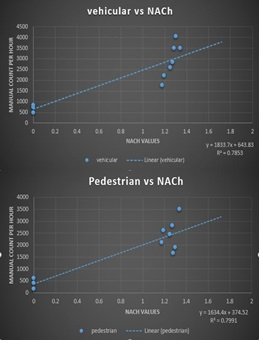
In this context, the results of the spatial analysis were superimposed with manual field observations to validate the process. These values were used to generate scatterplots using both spatial analysis and field observations of 10 gated counts at peak. According to spatial syntax theory, there is a strong correlation analysis for analysis values between 0.6 and 0.8. For this research, the correlation coefficient was found to be R2=0.7991, showing a strong positive correlation.
Space syntax methodology was therefore established to be consistent and acceptable in the decision-making process related to transportation network planning.
Figure 7
Regression analysis for pedestrian and vehicular data
Results and Conclusion
Through the investigation of spatial composition, spatial syntax aids in understanding the features of the research region. Results of spatial analysis are used to make more precise recommendations about where bus stops should be placed. Mansehra City measures two key factors. Using the city activity index, one may determine the optimal route, and the centrality index, and the other, the ideal place for bus stops. Spatial composition analysis was performed twice to obtain results for these indices. The first measured urban activity on a global scale of radius N (r=n) and the second measured urban centrality on a local scale of radius 5. , r=5.
Urban activity measurements helped identify stronger movement patterns in urban streets revealing potential routes/roads. By measuring the urban centrality index, you can identify areas that can be considered primary and secondary centres of activity throughout the city. It, therefore, represents an evidence- and science-based approach for determining bus stop distances in urban planning, and the results and methods of this study may contribute to the optimal positioning of bus stops in general and the city of Mansehra in particular for an efficient public transport system.
References
- Alterkawi, M. M. (2006). A computer simulation analysis for optimizing bus stops spacing: The case of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Habitat International, 30(3), 500–508.
- Ammons, D. (2014). Municipal benchmarks: assessing local performance and establishing community standards. Routledge.
- Bertonlini, L., & Spit, T. (1998). Cities on Rails: The Development of Railway Stations and Their Surroundings: E & FN Spon.
- Chien, S. I., & Qin, Z. (2004). Optimization of bus stop locations for improving transit accessibility. Transportation Planning and Technology, 27(3), 211– 227.
- El-Shair, I. M. (2003). GIS and remote sensing in urban transportation planning: a case study of Birkenhead, Auckland. In Map India Conference (pp. 167–181)
- Enström, R., & Netzell, O. (2007). Can Space Syntax Help Us in Understanding the Intraurban Office Rent Pattern? Accessibility and Rents in Downtown Stockholm. The Journal of Real Estate Finance and Economics, 36(3), 289– 305.
- Farwell, R. G., & Marx, E. (1996). Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation of OmniRide Demand-Driven Transit Operations: Feeder and Flex-Route Services. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 1557(1), 1–9.
- Fletterman, M. (2008b). Multi-Realization of Nonlinear Systems. University of Pretoria, Thesis
- Guihaire, V., & Hao, J.-K. (2008). Transit network design and scheduling: A global review. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 42(10), 1251–1273.
- Hansen, W. G. (1959). How Accessibility Shapes Land Use. Journal of the American Institute of Planners, 25(2), 73–76.
Cite this article
-
APA : Zobia., Ullah, U., & Ullah, S. (2023). A Planning Study on Spatial Attributes of Bus Stop Location for Efficient Public Transportation System. Global Social Sciences Review, VIII(I), 365-374. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2023(VIII-I).33
-
CHICAGO : Zobia, , Ubaid Ullah, and Shabbir Ullah. 2023. "A Planning Study on Spatial Attributes of Bus Stop Location for Efficient Public Transportation System." Global Social Sciences Review, VIII (I): 365-374 doi: 10.31703/gssr.2023(VIII-I).33
-
HARVARD : ZOBIA., ULLAH, U. & ULLAH, S. 2023. A Planning Study on Spatial Attributes of Bus Stop Location for Efficient Public Transportation System. Global Social Sciences Review, VIII, 365-374.
-
MHRA : Zobia, , Ubaid Ullah, and Shabbir Ullah. 2023. "A Planning Study on Spatial Attributes of Bus Stop Location for Efficient Public Transportation System." Global Social Sciences Review, VIII: 365-374
-
MLA : Zobia, , Ubaid Ullah, and Shabbir Ullah. "A Planning Study on Spatial Attributes of Bus Stop Location for Efficient Public Transportation System." Global Social Sciences Review, VIII.I (2023): 365-374 Print.
-
OXFORD : Zobia, , Ullah, Ubaid, and Ullah, Shabbir (2023), "A Planning Study on Spatial Attributes of Bus Stop Location for Efficient Public Transportation System", Global Social Sciences Review, VIII (I), 365-374
-
TURABIAN : Zobia, , Ubaid Ullah, and Shabbir Ullah. "A Planning Study on Spatial Attributes of Bus Stop Location for Efficient Public Transportation System." Global Social Sciences Review VIII, no. I (2023): 365-374. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2023(VIII-I).33
