Abstract
The demand for counterfeit goods has exponentially grown and counterfeit goods trade has consequently emerged as a global problem. The present study investigates the determinants that encourage consumers to acquire counterfeit luxury goods. This research further analyzes purchase intention as mediator and gender role as a moderator between the contextual factors and consumer behavior. A quantitative approach was applied through a questionnaire to gather data from 380 Pakistani respondents. The measurement and structural model assessed through Smart PLS. The results confirmed that purchase intention acts as a mediator between hedonic motives, materialism and consumer behavior. However, purchase intention has no mediating effect on economic benefits. Similarly, gender role as moderator was insignificant.
Key Words
Consumer Behavior, Counterfeit Luxury Goods, Gender, Pakistan, Purchase Intention.
Introduction and Background
Counterfeiting is a centuries-old phenomenon and one of the oldest examples of counterfeiting is the fake coins which were common in the Roman era. “The total value of global counterfeiting has reached 1.2 trillion USD in 2017 and is bound to reach 1.82 trillion USD by the year 2020” (Research and Markets, 2018). Pakistan comes in the top ten countries of the world wherefrom most fake goods originate (OECD/EUIPO, 2016) and counterfeit goods are easily available and sold openly (Ahmad, Yousif, Shabeer, & Imran, 2014).
Despite the extensive research on counterfeiting in developed countries, no study can be found to determine the causes of counterfeit purchases in Pakistan. This study played an important role in filling this research gap. Firstly, we developed a theoretical model based on contemporary literature to explore the determinants that encourage individuals to buy counterfeit luxury goods. Secondly, we extended the scope of the literature by applying and validating the TRA and TPB on counterfeit luxury goods. Thirdly, we focused on purchase intention as a possible mediator between economic benefits, hedonic motives, materialism and consumer behavior. Furthermore, we used demographic variable gender as a moderator to understand the gender base purchase differences. Lastly, remedies were suggested to anti-counterfeit organizations to overcome this unlawful business practice. The findings will be helpful for the governments, marketing professionals and policymakers who are trying to overcome counterfeiting.
Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
Counterfeiting
The Pakistan Penal Code Section 28 defines counterfeiting as, "A person is said to counterfeit who causes one thing to resemble another thing, intending by means of that resemblance to practice deception, or knowing it to be likely that deception will thereby be practised" (Pakistan Penal Code Act, 1860). The contemporary literature identified three categories of counterfeiting (i) deceptive (ii) non-deceptive and (iii) blur counterfeiting. In deceptive form of counterfeiting, individuals are unaware that the product purchased by them is counterfeit (Phau & Teah, 2009). However, “one-third of consumers would intentionally purchase counterfeit luxury goods and this type of counterfeit purchase is known as non-deceptive counterfeiting” (Amaral & Loken, 2016; Bian et al., 2016). Non-Deceptive counterfeiting mostly exists in luxury goods (Nia & Zaichkowsky, 2000).
In blur type of counterfeiting, consumers are confused about whether the goods they are buying are counterfeit or original (Bian, 2006).
The Effect of Economic Benefits on Purchase Intention and Consumer Behavior
Consumers value the economic benefits of counterfeit because the price considerably influences the consumer’s decision when opting for a counterfeit product (Gentry, Putrevu, & Shultz, 2006). Consumers always prefer to pay a lower price with certain acceptable standards of product quality Ang et al., (2001) and would prefer a counterfeit product instead of a genuine brand if the price difference is significant (Bian & Moutinho, 2009; Bloch). Due to these factors, we presented the hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1: Economic benefits effect significantly and positively the counterfeit luxury goods purchase intention.
Hypothesis 2: Economic benefits effect significantly and positively the counterfeit luxury goods purchase behavior.
The Effect of Hedonic Motives on Purchase Intention and Consumer Behavior
Hedonic motives are another important factor that encourages consumers to purchase products (Kang & Park-Poaps, 2010). Consumers consider luxury goods as a novel, status symbol and try to match them with their personality and therefore consumers get attracted and purchase counterfeit goods. (Penz & Sto¨ttinger, 2008). Therefore, we postulated the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 3: Hedonic motives effect significantly and positively the counterfeit luxury goods purchase intention.
Hypothesis 4: Hedonic motives effect significantly and positively the counterfeit luxury goods purchase behavior.
The Influence of Materialism on Purchase Intention and Consumer Behavior
Consumers with materialistic traits give relatively high importance to owning possessions (Belk, 1985). They are highly concerned about exhibiting their possessions to other people or groups to flaunt their high status in society (Fitzmaurice & Comegys, 2006). They consider material goods, as valuable to acquire centrality, success and happiness in life (Richins, 1994). Therefore, we presented the hypotheses:
Hypothesis 5: Materialism effect significantly and positively the counterfeit luxury goods purchase intention.
Hypothesis 6: Materialism effect significantly and positively the counterfeit luxury goods purchase behavior.
Mediating Role of Purchase Intention
This research seeks to determine whether purchase intention acts as a mediator between the independent variables (economic benefits, hedonic motives & materialism) and the dependent variable (consumer behavior). Past studies have provided the theoretical background for the mediation effect of purchase intention on consumer behavior (De Matos, Ituassu, & Rossi, 2007). Therefore, we proposed that purchase intention plays a mediating role. The proposed hypothesis is:
Hypothesis 7: Purchase intention mediates the relationship between contextual variables and consumer behavior.
Moderating Role of Gender
Recent studies confirmed gender differences exist and researchers like Singhapakdi, (2004), highlighted that comparatively female respondent was more ethical than male. Similarly, Kwong, Yau, Lee, Sin, & Tse, (2003) found males were comfortable in purchasing counterfeit CDs as compared to females. If gender difference patterns exist, it is important for marketers to investigate them to develop a more appropriate gender-based strategy to fight against counterfeit activities. Therefore, the proposed hypothesis is:
Hypothesis 8a: Gender positively moderates the relationship between contextual variables and intention.
Hypothesis 8b: Gender positively moderates the relationship between contextual variables and consumer behavior.
Theoretical Framework
This study draws theoretical support to analyzed counterfeit luxury goods purchasing behavior from reasoned action and planned behavior theories. The research model posits a total of five variables, purchase intention presented as a mediating variable between independent and dependent variables. Furthermore, gender studied as a moderator variable between contextual variables and purchase intention along with consumer behavior. The proposed model presented in Figure 1 (on next page)
Figure 1
The Proposed Model
Research Methodology
Research design
Data was collected from Pakistani consumers based in Pakistan. A sample composed of 380 respondents were gathered. The collected sample was evenly distributed on a gender basis (190 males and 190 females). The respondents were selected through a non-probability snowball sampling technique.
Measures
The research questionnaire consisted of a total of 40 items with five variables plus demographic analysis. The selected constructs were adapted from established and cross-nationally validated scales. The variable economic benefits were measured with six items adapted from Lee and Yoo (2009), hedonic motives with ten items measured by using scale developed by Babin et al., (1994), materialism measured by using nine items of Richins (1994) materialism scale, purchase intention with four items measured by using an adapted scale of De Matos et al., (2007), consumer behavior was measured with five items adapted from Fan, Lan, Huang, and Chang, (2013). These constructs were measured through five-point Likert scale, where 1 “strongly disagree” and 5 “strongly agree”. The demographic characteristics consisted of gender, age, location, qualification, occupation, and monthly income.
Data Analysis
The measurement and structural model assessed through Smart PLS Version 3.2.8. PLS is a recommended technique to simultaneously measure regression and confirmatory factor analysis (Garson, 2016). The data were first examined for missing values and for this purpose a widely accepted list-wise deletion method was selected.
Descriptive Statistics
The demographic characteristics analysis indicated that the selected sample of the population primarily consists of a young, educated, salaried class with quite reasonable income level and equally distributed on gender basis across Pakistan. Presented below in Table 1.
Table 1. Descriptive Statistics
Demographic Variables | Description | Frequency | Percent |
Gender | Male | 190 | 50.0 % |
Female | 190 | 50.0 % | |
Age (in years) | 13 to 19 | 4 | 1.1 % |
20 to 30 | 105 | 27.6 % | |
31 to 40 | 205 | 53.9 % | |
41 to 50 | 52 | 13.7 % | |
51 and above | 14 | 3.7 % | |
Location | Federal Area | 122 | 32.1 % |
Punjab | 144 | 37.9 % | |
Sindh | 17 | 4.5 % | |
Baluchistan | 11 | 2.9 % | |
KPK | 61 | 16.1 % | |
Others | 25 | 6.6 % | |
Qualification | Matric or below | 0 | 0 % |
Under Graduate | 11 | 2.9 % | |
Graduate | 147 | 38.7 % | |
Post Graduate | 222 | 58.4 % | |
Occupation | Student | 39 | 10.3 % |
Salary Person | 315 | 82.9 % | |
Business People | 3 | 0.8 % | |
Housewife | 23 | 6.1 % | |
Income Per Month (in PKR) | Below 25,000/- | 63 | 16.6 % |
26,000/- to 50,000/- | 79 | 20.8 % | |
51,000/- to 75,000/- | 75 | 19.7 % | |
76,000/- to 100,000/- | 62 | 16.3 % | |
Above 100,000/- | 101 | 26.6 % |
Empirical Results
The skewness and kurtosis values are important in the analysis of behavioral research data. The recommended best fit range of kurtosis is ± 2 (Gravetter & Wallnau, 2014). The research data confirmed that all constructs were within the recommended best fit range of kurtosis as presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Mean, SD, Skewness, Kurtosis, and Items Description
Variables | Mean | Std. Deviation | Skewness | Kurtosis | Items |
Economic Benefits (EB) | 3.31 | 1.02 | -.19 | -1.175 | 06 |
Hedonic Motive (HM) | 3.10 | 1.01 | .24 | -1.120 | 10 |
Materialism (M) | 2.96 | 1.03 | .51 | -1.046 | 09 |
Purchase Intention (PI) | 3.39 | 0.97 | .13 | -1.036 | 04 |
Consumer Behavior (CB) | 3.52 | 0.96 | -.44 | -.674 | 05 |
The diagonal values shown in table 3 represented the square roots of the AVEs, and all values were higher than the correlation value of these constructs. Therefore, the results supported the good discriminant and convergent validity of the data.
Table 3. Bi-variate Correlations, Descriptive and Discriminant Validity
Variables | Mean | S.D | EB | HM | M | PI | CB |
EB | 3.31 | 1.02 | 0.901 |
|
|
|
|
HM | 3.10 | 1.01 | .424** | 0.917 |
|
|
|
|
| .000 |
|
|
|
| |
M | 2.96 | 1.03 | .283** | .034 | 0.875 |
|
|
|
| .000 | .695 |
|
|
| |
PI | 3.39 | 0.97 | .306** | .399** | .224** | 0.965 |
|
|
| .000 | .000 | .000 |
|
| |
CB | 3.52 | 0.96 | .408** | .433** | .316** | .548** | 0.934 |
|
| .000 | .000 | .000 | .000 |
| |
**Correlation significant at 0.05 level (2-tailed). Diagonal values represent square root of AVE. N = 380 EB=Economic Benefits, HM=Hedonic Motives, M=Materialism, PI= Purchase Intention, CB = Consumer Behavior. | |||||||
The Measurement Model
The proposed measurement model consisted of a total of five variables. In the reflective measurement model, none of the latent variables has unidirectional paths. Each latent variable was connected to others and the covariance of the variables was estimated, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2
The Measurement Model
Figure 2
The Measurement Model
The composite reliability (CR) examine the overall reliability of selected heterogeneous but similar items. A CR value above 0.70 is enough to demonstrate internal consistency and reliability (Hair, Hult, Ringle, & Sarstedt, 2016). As mentioned in Table 4. Convergent validity was measured through the value of the average variance extracted (AVE). The acceptable range for AVE value is above 0.50 Hair et al., (2016). Results confirmed that AVE values were above the acceptable range. As shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Results of the Measurement Model
Latent Variable
| Indicator’s
| Factor Loadings
| Cronbach's Alpha (?) | Composite Reliability (CR) | Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
Economic Benefits (EB)
| EB1 | 0.927 | 0.954 | 0.963 | 0.813 |
EB2 | 0.925 | ||||
EB3 | 0.934 | ||||
EB4 | 0.920 | ||||
EB5 | 0.882 | ||||
EB6 | 0.815 | ||||
Hedonic Motives (HM) | HM1 | 0.912 | 0.979 | 0.982 | 0.841 |
HM2 | 0.929 | ||||
HM3 | 0.911 | ||||
HM4 | 0.910 | ||||
HM5 | 0.918 | ||||
HM6 | 0.899 | ||||
HM7 | 0.932 | ||||
HM8 | 0.931 | ||||
HM9 | 0.923 | ||||
HM10 | 0.907 | ||||
Materialism (M)
| M1 | 0.865 | 0.962 | 0.967 | 0.765 |
M2 | 0.903 | ||||
M3 | 0.874 | ||||
M4 | 0.911 | ||||
M5 | 0.869 | ||||
M6 | 0.867 | ||||
M7 | 0.846 | ||||
M8 | 0.886 | ||||
M9 | 0.848 | ||||
Purchase Intention (PI)
| P1 | 0.966 | 0.975 | 0.982 | 0.931 |
P2 | 0.962 | ||||
P3 | 0.959 | ||||
P4 | 0.973 | ||||
Consumer Behavior (CB)
| CB1 | 0.924 | 0.963 | 0.971 | 0.872 |
CB2 | 0.949 | ||||
CB3 | 0.936 | ||||
CB4 | 0.923 | ||||
CB5 | 0.937 |
The Structural Model
The R² value estimated for purchase intention (mediating variable) and consumer behavior (dependent variable) were 0.212 and 0.418 respectively, these values suggested 21.2% and 41.8% of the variance. These results provided support for a satisfactory and substantial model. The proposed hypotheses were tested through the non-parametric bootstrapping process. A re-sample of 5,000 was processed to obtain the standard error. The path coefficient and t-values are shown in Figure 3 and Table 5.
Figure 3
Main Effect Model
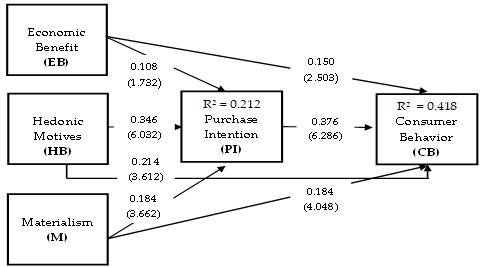
The analysis of path coefficient’s results confirmed that economic benefits (EB) has no direct and significant impact on purchase intention (PI) (? = 0.108; t = 1.732; p = 0.083). The results indicated to reject Hypothesis 1. The path coefficient’s results of economic benefits (EB) has a direct and significant positive impact on consumer behavior (CB) (? = 0.150; t = 2.503; p < 0.05). The results supported the proposed hypothesis and based on that Hypothesis 2 accepted. The path coefficient’s results of hedonic motives (HB) has a direct and significant impact on purchase intention (PI) (? = 0.346; t = 6.032; p < 0.05). The results confirmed the proposed hypothesis and based on that Hypothesis 3 accepted. The path coefficient’s results of hedonic motives (HB) has a direct and significant positive impact on consumer behavior (CB) (? = 0.214; t = 3.612; p < 0.05). Based on these results Hypothesis 4 accepted. The path coefficient’s results of materialism (M) has a direct and significant positive impact on purchase intention (PI) (? = 0.184; t = 3.662; p < 0.05). The results supported the proposed hypothesis and based on that Hypothesis 5accepted. The path coefficient’s results of materialism (M) has a direct and significant positive impact on consumer behavior (CB) (? = 0.184; t = 4.048; p < 0.05). Based on these results Hypothesis 6 accepted. The path coefficient’s results of purchase intention (PI) has a direct and significant positive impact on consumer behavior (CB) (? = 0.376; t = 6.286; p < 0.05). The supported the proposed hypothesis and based on these results Hypothesis 7 accepted.
Table 5. Regression Weights
Models | Original Sample | Mean (M) | Standard Deviation (STDEV) | T Statistics (|O/STDEV|) | P Values | Status |
EB ->PI | 0.108 | 0.108 | 0.062 | 1.732 | 0.083 | Rejected |
EB ->CB | 0.150 | 0.150 | 0.060 | 2.503 | 0.012 | Accepted |
HM ->PI | 0.346 | 0.346 | 0.058 | 6.032 | 0.000 | Accepted |
HM ->CB | 0.214 | 0.214 | 0.059 | 3.612 | 0.000 | Accepted |
M ->PI | 0.184 | 0.184 | 0.050 | 3.662 | 0.000 | Accepted |
M ->CB | 0.184 | 0.184 | 0.045 | 4.048 | 0.000 | Accepted |
PI ->CB | 0.376 | 0.376 | 0.060 | 6.286 | 0.000 | Accepted |
EB=Economic Benefits, HM=Hedonic Motives, M=Materialism, PI= Purchase Intention, CB = Consumer Behavior.
The Mediating Analysis of Purchase Intention
The mediating analysis confirmed that purchase intention (PI) has no mediating effect between economic benefits (EB) and consumer behavior (CB) (? = 0.041; t = 1.6661; p < 0.05). However, purchase intention (PI) mediates the relationship between hedonic motivation (HM) and consumer behavior (CB) (? = 0.130; t = 4.208; p < 0.05). Similarly, purchase intention (PI) mediates the relationship between materialism (M) and consumer behavior (CB) (? = 0.069; t = 2.905; p < 0.05). Results confirmed that purchase intention has a mediating effect between hedonic motives, materialism and consumer behavior. While purchase intention has no mediating effect with economic benefits and consumer behavior as presented in table 6.
Table 6. Mediating Analysis
Models | Path (A) | Path (B) | A*B | t-Value | Status |
EB -> PI -> CB | 0.108 | 0.376 | 0.041 | 1.666 | Insignificant |
HM -> PI -> CB | 0.346 | 0.376 | 0.130 | 4.208 | Significant |
M -> PI -> CB | 0.184 | 0.376 | 0.069 | 2.905 | Significant |
EB=Economic Benefits, HM=Hedonic Motives, M=Materialism, PI= Purchase Intention, CB = Consumer Behavior.
The Moderating Analysis of Gender
The results for moderating variable gender demonstrated insignificant in either regression equation or none of the value falls within the acceptable range of P-Value i.e. (p < 0.05) as mentioned in Table 7. The results support previous studies where Schiffman & Kanuk, (2004) mentioned: “sex roles have blurred, and gender is no longer an accurate way to distinguish consumers in some product categories”. Similarly, Butler, (2011) argue that gender has no place in consumer research and should be abandoned. Based on these results both hypothesis 8a and hypothesis 8b were rejected.
Table 7. Moderating Analysis
Models | Path Coefficients (Female) | Path Coefficients (Male) | Path Coefficients Difference (Male-Female) | P Values | Status |
EB -> PI | 0.130 | 0.085 | 0.045 | 0.642 | Rejected |
EB -> CB | 0.073 | 0.227 | 0.154 | 0.093 | Rejected |
HM -> PI | 0.362 | 0.330 | 0.032 | 0.612 | Rejected |
HM-> CB | 0.176 | 0.248 | 0.072 | 0.272 | Rejected |
M -> PI | 0.116 | 0.253 | 0.137 | 0.076 | Rejected |
M -> CB | 0.203 | 0.172 | 0.031 | 0.638 | Rejected |
PI -> CB | 0.479 | 0.281 | 0.198 | 0.947 | Rejected |
EB=Economic Benefits, HM=Hedonic Motives, M=Materialism, PI=Purchase Intention, CB=Consumer Behavior
Discussion
The results indicated that hedonic motives and materialism have a positive impact on counterfeit luxury goods purchase intention and consumer behavior. These results matched with past studies (Erg?n, 2010; Kaufmann et al., 2016; Li, Lam, & Liu, 2018; Lianto, 2015). While economic benefits are insignificant to purchase intention, they are positively related to consumer behavior. The results are again consistent with the previous work done by Bian & Moutinho, (2009); Kwong et al., (2003); Stravinskiene, Dovaliene, & Ambrazeviciute, (2013) which reported that consumers’ counterfeit purchase intention was not purely dependent on income. Similarly, results were unable to find any moderating effects of gender. The result of the non-significant role of gender support the previous research conducted by Hegarty & Sims, (1978); Schiffman & Kanuk, (2004); Singhapakdi & Vitell, (1990), mentioned the limited role of gender to differentiate consumers in some product categories.
Theoretical Contribution
Our research makes several theoretical contributions. First and foremost, this research work successfully applied behavioral theories TRA and TPB to study purchase intention leading to consumer purchase behavior. The study also develops a theoretical model by testing and validating the determinants responsible for purchase behavior towards counterfeit luxury goods. Past studies on this issue primarily covered the markets of advanced countries and very few studies explored developing economies like Pakistan. Perhaps this is the only study in the domain of counterfeit luxury goods that have successfully incorporated purchase intention and gender as mediator moderator in a single model. Thus, the proposed and empirically tested model will help the stakeholders understand why consumers have positive purchase behavior towards counterfeiting in Pakistan.
Practical Implication
Ant counterfeit policymakers may wish to determine what can be done to restrain the ever-growing trend of buying counterfeit goods. Our research confirmed that materialism and hedonic motives effect positively to counterfeit purchase intention. Both these variables were related to the display of wealth and a sense of excitement. Therefore, marketers should develop policies to counter the counterfeit goods purchased only for the purpose of status seeking, fun and excitement (Bhardwaj, 2010). Brand owners should develop awareness about ethical purchasing behavior by discouraging consumers regarding the harmful impacts of counterfeit goods. The original brand owners should start educating consumers about the benefits associated with original luxury brands through marketing activities, such as seminars, workshops and special events.
Limitations and Directions for Future Research
The selected sample cannot be claimed that it is a perfect representation of all Pakistani consumers. A major limitation of cross-sectional research analysis is that it represents views in relation to a specific time period. Similarly, the selected scale used in the current research may not produce the same results with other counterfeit goods. The theoretical model and data may or may not produce the same results in other countries. Another limitation is that it covered only counterfeit luxury goods and if the same parameter applied on other types of counterfeit products like food, medicines, and auto parts, it may result in more unfavorable consumer behavior towards counterfeits. Finally, this study is time and money constraint.
Some of the recommendations for future researchers are to study the post-purchase behavior that will help in understanding consumer’s feelings after using these goods. Future researchers can examine those consumers who exclusively buy counterfeit goods online and can even make a comparison of online purchasing with traditional purchasing of counterfeit goods. They can also use the same model in other countries where cultural differences exist. Another suggestion for future researchers is to observe the actual behaviors and emotions of the consumers through an experiment with real customers and retailers.
References
- Ahmad, N., Yousif, M., Shabeer, K., & Imran, M. (2014). A Comprehensive Model on Consumer's Purchase Intention towards Counterfeit Mobiles in Pakistan. Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research, 4(5), 131-140.
- Amaral, N. B., & Loken, B. (2016). Viewing usage of counterfeit luxury goods: Social identity and social hierarchy effects on dilution and enhancement of genuine luxury brands. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 26(4), 483-495.
- Ang, S. H., Cheng, P. S., & Lim, E. A. C. (2001). Spot the difference : consumer responses towards counterfeits. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 18(3), 219-235.
- Babin, B. J., Darden, W. R., & Griffin, M. (1994). Work and/or Fun : Shopping Measuring Value Hedonic and Utilitarian Shopping Value. Journal of Consumer Research, 20(4), 644-656.
- Beck, L., & Ajzen, I. (1991). Predicting dishonest actions using the theory of planned behavior. Journal of Research in Personality, 25(3), 285-301.
- Belk. (1985). Materialism: Trait Aspects of Living in the Material World. Journal of Consumer Research, 12(3), 265-280.
- Bian, X. (2006). An examination of factors influencing the formation of the consideration set and consumer purchase intention in the context of non-deceptive counterfeiting. PhD Thesis, (October 2006).
- Bian, X., & Moutinho, L. (2009). An investigation of determinants of counterfeit purchase consideration. Journal of Business Research, 62(3), 368-378.
- Bian, X., Wang, K. Y., Smith, A., & Yannopoulou, N. (2016). New insights into unethical counterfeit consumption. Journal of Business Research, 69(10), 4249-4258.
- Bloch, P. H., Bush, R. F., & Campbell, L. (1993). Consumer
- Butler, J. (2011). Gender Trouble: Feminism and the Subversion of Identity. Routledge 270 Madison Avenue, New York, NY 10016.
- Cordell, V. V, Wongtada, N., & Kieschnick, R. L. J. (1996). Counterfeit Purchase Intentions
- De Matos, C. A., Ituassu, C. T., & Rossi, C. A. V. (2007). Consumer attitudes toward counterfeits: A review and extension. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 24(1), 36-47.
- Eisend, M., & Schuchert-Guler, P. (2006). Explaining counterfeit purchases: A review and preview. Academy of Marketing Science Review, 12(6), 1-25.
- Ergın, E. A. (2010). The rise in the sales of counterfeit brands: The case of Turkish consumers. African Journal of Business Management, 4(10), 2181-2186.
- Fan, W., Lan, C., Huang, Y., & Chang, R. (2013). A study on purchasing behavior of teenagers in Taiwan : example of counterfeit goods. Journal OfApplied Social Psychology 2013, 43, 1289-1300.
- Fitzmaurice, J., & Comegys, C. (2006). Materialism and Social Consumption. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 14(4), 287-299.
- Garson, G. D. (2016). Partial Least Squares: Regression and Structural Equation Models. Statistical Publishing Associates. 274 Glenn Drive Asheboro, NC 27205 USA. Retrieved from
- Gentry, J. W., Putrevu, S., & Shultz, C. J. (2006). The effects of counterfeiting on consumer search. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 256(June), 245-256.
Cite this article
-
APA : Saeed, A., & Paracha, O. S. (2019). The Determinants Influencing the Influx of Counterfeit Luxury Goods in Pakistan. <i>Global Social Sciences Review, IV(II)</i>, 211-221. <a href='https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-II).28'>https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-II).28</a>
-
CHICAGO : Saeed, Abid, and Osman Sadiq Paracha. 2019. "The Determinants Influencing the Influx of Counterfeit Luxury Goods in Pakistan." <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i>, IV (II): 211-221 doi: 10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-II).28
-
HARVARD : SAEED, A. & PARACHA, O. S. 2019. The Determinants Influencing the Influx of Counterfeit Luxury Goods in Pakistan. <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i>, IV, 211-221.
-
MHRA : Saeed, Abid, and Osman Sadiq Paracha. 2019. "The Determinants Influencing the Influx of Counterfeit Luxury Goods in Pakistan." <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i>, IV: 211-221
-
MLA : Saeed, Abid, and Osman Sadiq Paracha. "The Determinants Influencing the Influx of Counterfeit Luxury Goods in Pakistan." <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i>, IV.II (2019): 211-221 Print.
-
OXFORD : Saeed, Abid and Paracha, Osman Sadiq (2019), "The Determinants Influencing the Influx of Counterfeit Luxury Goods in Pakistan", <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i>, IV (II), 211-221
-
TURABIAN : Saeed, Abid, and Osman Sadiq Paracha. "The Determinants Influencing the Influx of Counterfeit Luxury Goods in Pakistan." <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i> IV, no. II (2019): 211-221. <a href='https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-II).28'>https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-II).28</a>
