Abstract
The current study is conducted to evaluate the e-government portal E-Khidmat Markaz launched by the government of Punjab. This study addresses two contemporary issues related to e-government: the successful implementation and the factors behind the success. For this purpose, a theoretical framework for assessing critical success factors behind e-government and online interaction in Pakistan is developed. The responses of 25 officials from public sector firms were interviewed to determine the relationships between technological, organisational, and external factors and the successful implementation of e-government. The nature of the study is qualitative, and the research methodology is applied using Nvivo software. This study will contribute to the research work done in the IT sector and the managerial implications of adopting e-government-based service delivery. The Pakistani government can realise its advancement through proper planning, policymaking, process designing, and improving it. Government-based services can be delivered more effectively and efficiently. A citizen will be more satisfied with a government organisation's performance if the factors identified in the study given consideration will implement in an e-government project in Pakistan.
Key Words
E-government, Policy Planning, Online Interaction, IT Vendors
Introduction
The technological advancement of the new era is transforming our way of living in a revolutionary manner, and the change is not limited to our personal lives but is also advanced to our social interactions, formal dealings, and day-to-day operations we conduct. The way in which citizens interact with a government official for getting their official work, marriage certificate, birth certificate, death certificate licenses and tax return filing, etc., was manual and paper-based, but now online government-based portals have replaced that traditional ways of facilitating citizens. The technological revolution started to take place with the commencement of the 21st century, but in the government sector, it was initiated in 2012 with serious intentions. The measures the government has taken in Pakistan to promote technological infrastructure development and related know-how are in their initial stages. Proper development and implementation of these IT-related plans will not only modernise the way of working but will also be cost-effective and efficient. E-government is called Digital government, Electronic government, and online government as well. According to Fang (2002), to understand the terminology E-Government, we should simply consider it a web-based application of the internet, which is innovative and employs information technology for the purpose of facilitating citizens with information .access to online convenient government services. The service quality is not only improved but also provides more opportunities to use plenty of information in a productive manner, such as the processes can be improved by providing timely feedback. Online portals are means of active communication. Furthermore, this timely information is provided on an equal basis; every individual can possess it as required. The working efforts of the government sector can be aligned to create synergy, reduce costs stronger and model IT implications, enhance facilitation, and increase facilitation to citizens.
The current study involves 'E-Khidmat Markaz' as the subject of interest, which is an integrated web-based portal including different government-based services associated with different government departments and provided on a single platform. The online services of E-government portals are started in Punjab cities Multan, Lahore, Rawalpindi, Bahawalpur, Sargodha, Sahiwal Gujranwala, and Faisalabad. The number of received requests/applications and executed actions are displayed on the portal with updates. The applications can be related to licenses of vehicles, utility bills, divorce certificates, birth certificate route permits, taxation domicile, excise, and computerised national identity cards .this initiative has been taken under the supervision of the Chief Minister of Punjab, which is restricted to solve the queries within eight days. The plan included 11 cities in Punjab; it was successfully implemented in eight mentioned cities
Literature Review
The lives of people are changed because of the transformation information technology has made, like communication patterns are upgraded in addition to interaction methods of government with its citizens in the whole world (Lee, 2010). The researchers and the practitioners in the field of information technology have become attentive to this IT revolution in the same context. This specific field is more suitable for conducting research. (Chen, Chen, Huang, and Ching, 2006). The common reason to study E-Government in a repetitive manner is to explore its factors related to cost-effectiveness, operational efficiency, complexity reduction, and smoothing the formal procedures. (Basu, 2004). The E-Government implementation is now regarded as the main concern in terms of policy formulation by many countries, and in the same manner, resources are allocated, and efforts are directed towards its promotion and usage by citizens.
Pakistan is a developing country with an inherited low literacy rate, poor infrastructure, and fewer government services provided to its inhabitants by virtue of its location; its neighbouring countries also face these problems. The south Asian countries possess fewer infrastructural facilities and low acceptance of changing technology which is a strong cultural barrier in the way of development, so we can argue about the introductory phase of IT development in these countries. Almakki (2009), the infrastructure alone cannot help if proper guiding principle top to down hierarchy is not fully involved and support is shown in policies, processes, and actions taken at the time of implementation. Qaiser and Khan (2010) argue in support of the commitment of top-level management to the ongoing and facilitative execution of projects related to e-government. The budget allocation for projects is seen in the case of Pakistan, which is a hurdle in the way of e-government projects.
The political problems, along with the financial assistance issue, increase the severity of problems in which projects are least likely to be successful. For instance, projects face delays or closer ultimately at the expense of already invested resources. The frequently changing governments do not continue beneficial projects of opponent political parties (Rehman et al., 2012). There are many services that are provided by the government to the Pakistani nation. At the same time system is facing problems related to IT infrastructure, IT facilities, and systemic organisation. The internet facilities are not enough, security issues are problematic, and the absence of proper IT policies make initiatives least progressive Kayani et al. (2011). Organisational efficiency can be achieved through e-government implementation to take advantage of better service delivery and more comprehensive deployment of IT infrastructure. Effective work can be done by having full control over manual and automatic methods of data generation, process evaluation, knowledge management, and auditing.
The Research Problem
The success of e-government is always dependent upon some critical success factors. In the scenario of Pakistani, few studies concentrate on success factors. This study is conducted to highlight critical success factors which affect the implementation of e-government programs successfully. The specific problem statement of this study is as follows;
The identification of success factors involved in the successful launch and working of the e-government portal, i.e., "E Khidmat Markaz" in Punjab provinces of Pakistan.
Research Objectives
The objectives of the study are specific to the
following points:
1. To identify technological factors of e-government and online citizen interaction in Pakistan
2. To identify organisational factors of e-government and online citizen interaction in Pakistan
3. To identify environmental factors of e-government and online citizen interaction in Pakistan
4. To explore the significance of each kind of factor of e-government and online citizen interaction in Pakistan.
5. To give general recommendations to public sector organisations and consultants for the e-government and online citizen interaction in Pakistan
Research Question
Q1: What are the technological factors behind the success of E-government and online citizen interaction in Pakistan?
Q2: What are the organisational factors behind the success of E-government and online citizen interaction in Pakistan?
Q3: What are the environmental factors behind the success of E-government and online citizen interaction in Pakistan?
Conceptual Framework
The TOE model has been used in the current study, which is a tool to analyse e-government implementation in a more comprehensive way; the following mentioned studies have employed the TOE model, which justifies its significance.
Table 1
|
Research
work |
Description
|
|
Hackney et al. (2006) |
Case study analysis of web sites
adoption In UK |
|
Kuan and Chau (2001) |
electronic data interchange (EDI)
related investigation in Hong Kong
firms |
Figure 1
Research Methodology
The case study approach has been employed in this study as an effective tool to research diverse cases. This approach is better suited for comprehensive and to-the-point data collection, information details, selecting a unique nature of the case, and knowledge building after getting results. The TOE model is employed to differentiate technological, environmental, and organisational factors to concentrate on each E-government aspect's influence. The Lahore-based government organisations are population, and four organisations are selected to draw the sample for the study. The services of these organisations are linked to the E-Khidmat Markaz portal.
Data Collection
The interviews were taken with 25 government officials, consisting of 20-30 minutes. The questions were made for interview protocol,
and the respondent was aided with sufficient information to understand the study's rationale and related knowledge /information to the topic. An interview is an effective tool for collecting data in qualitative research design. The participants are selected, questions are asked, and the obtained data is documented, analysed, processed, and reported findings.
Data Analysis
Word Tree Analysis
The word Technology must be considered as a keyword for the study because technology transforms the whole process of service delivery in a contemporary manner and converts Government to E-Government. The text search query was applied to explore "Technology." In figure 2, the word tree resulting technology word is shown, which points to the responses of respondents specifically for word technology. The study has explored success factors in terms of technology.

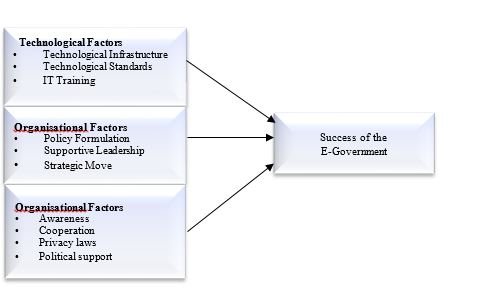
Treemap Analysis
The Treemap is used to analyse the different aspects of the data, which are displayed in relative sizes showing comparison and accruing in hierarchies. The liner study of responses is much more difficult as compared to rectangular shapes and sizes denoting labels mentioned on the chart. The expansion of the treemap provides an increased level of detail, and the significance of each theme can be easily understood. The current study's treemap can be seen in figure 3, specifically the success factors behind e-government. The TOE model involves the study of technological, organisational, and environmental factors. In the current study, the more influential Technological factors were technological infrastructure, technological standards, IT training, online content quality, and technical know-how. The organisational factors were policy formulation, supportive leadership, strategic move, need analysis, easy access, operational efficiency, skilled human resources, diverse facilities, and change management. The environmental factors included awareness, cooperation, privacy laws, good governance, culture, evaluation process, and local language.
Figure 3

Table 2
|
Aspect
|
Factors
|
|
Technological
|
·
Technological
infrastructure ·
Technological
standards ·
IT
training |
|
Organisational
|
·
Policy
formulation ·
Supportive
leadership ·
Strategic
move ·
Low
cost |
|
Environmental
|
·
Awareness
·
Cooperation
·
Privacy
laws ·
Political
support ·
Good
governance |
Word Clouds
The tag clouds in figure 5 depict the words used in the study more frequently and used by respondents again and again in textual data .to analyse the tag clouds results. One must consider the size of words as an analysis criterion. The bigger words are repeatedly used. In the current study, tag clouds are used twice to show results before and after the funnelling approach. The result shows problems, critical, common, related, improve, users, and years are words that do not make any sense to the theme or findings of the study, so we can consider these words meaningless. On the other hand, services, information policy change technology training, management government and stakeholders relate the investigation to the theme and are frequently used by respondents.
Figure 5
Word Clouds -Funneling Approach Applied
We can quickly analyse in figure 6 the reduction of useless words after applying the funnelling approach. The word clouds are more relevant and specific after applying funnelling. The meaningless words were added to the 'add to stop list' to eliminate the inclusion of such unnecessary words.


Discussion of Results
The e-government implementation in public sector organisations faces many problems at different levels. Still, the issues can be summarised as follows: 1) lack of collective efforts within the public sector organisations to make information more accessible and being rigid to information-sharing culture. 2) agency problem in government organisations to share information for the best interest of the general public.3) conflicting nature of political interests.
Considering the results of current studies, we can argue that in the context of Pakistan, the study's findings accurately represent the target factors to be addressed for e-government adoption, like technological infrastructure is the most critical factor to be addressed when we take into account Technological factors. The budget limitations do not allow basic technological infrastructures in rural areas of far Punjab. The developed cities like Lahore, Multan and Islamabad possess advanced IT infrastructure facilities. The technological backwardness of many areas in Punjab is because of political agendas, government policies, and corruption. The alignment of Shared information between citizens and Government organisations depends on standardised technology. Associated costs, transparency, and policy are also supported by the study of shaikh et al. (2016).
The human resources, training costs, and IT installations of hardware and software collectively can increase the budgeting of e-government projects when implemented at a higher level and in different cities, villages, towns, or areas of any province. This qualitative study was employed, and interviews revealed the importance of general awareness among people for adopting the technological aspect of government services. The policy-driven e-government initiatives must be taken to expand the piracy laws, data security, and users' trust. The time and cost associated with this service delivery must be reduced and political barriers eliminated. In the study conducted in Jordan, similar results are found, like technological standards and infrastructure related to information technology, privacy laws, security of information, the strategy of organisations, training, and leadership (Shboul et al., 2014). The concept of information privacy and law is new in Pakistan started in 2005 when actions related to intellectual property were taken (Bakir et al., 2009).
Recommendations
Taking into account the results of the current study, the recommendations can be given:
? The government services system to e-government must be conducted as a process involving restructuring.
? The general awareness about e-government and its usability must be conveyed.
? Following the best practices from the developed world during implementations in other big cities like Karachi, the success of the project will be achieved in a speedy way.
? The resource allocation and budget-making process must be initiated after careful cost-benefit analysis in small areas.
? To have political support, formal authorities must provide accurate information and rationale for e-government at the ministry level.
? The work efficiency and refined processes practised by the private sector can facilitate in construction of the base of e-government through a private-public partnership.
? The research funding must be increased to explore new and flexible ways of adopting e-government in the Pakistani scenario.
? The technological know-how and training sessions can increase the acceptability of e-government programs among less-educated clerical level public sector employees.
? A visionary approach can smoothly implement e-government projects in the country, achieving step-by-step millstones.
? The change management mechanism must award achievements and motivate initiatives.
Conclusion
Information technology can increase the efficiency of government departments. The service delivery process will be better performed with more informed citizens. The improvements can be made regarding time cost productivity, organisations, and feedback system. One size does not fit all the customised enhancements, and systems must be introduced for all regions to attain better results. The legal barriers and requirements must be carefully assessed to keep processes in control.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
References
- Almakki, R. (2009). Communities of practice and knowledge sharing in E-Government initiatives (Doctoral dissertation, The University of Manchester).
- Al-Shboul, M., Rababah, O., Al-Shboul, M., Ghnemat, R., & Al-Saqqa, S. (2014). Challenges and Factors Affecting the Implementation of E-Government in Jordan. Journal of Software Engineering and Applications, 7(13), 1111–1127.
- Baqir, M. N. (2009). A qualitative inquiry of ICT based socio-economic development in developing countries: The case of Pakistan. The University of North Carolina at Greensboro.
- Bilenko, M., Basu, S., & Mooney, R. J. (2004, July). Integrating constraints and metric learning in semi-supervised clustering. In Proceedings of the twenty-first international conference on Machine learning 11. ACM.
- Chen, Y. N., Chen, H. M., Huang, W., & Ching, R. K. (2006). E-government strategies in developed and developing countries: An implementation framework and case study. Journal of Glo Kayani, M. B., Haq, M. E., Perwez, M. R., & Humayun, H. (2011). Analysing barriers in e-Government implementation in Pakistan. International Journal for Infonomics, 4(3), 494-500. bal Information Management, 14(1), 23.
Cite this article
-
APA : Ahmed, S., Khalid, K. S., & Khalid, S. (2022). Success Factors of E-Government and Interaction with Electronic Portal in Pakistan: A Case Study Approach. Global Social Sciences Review, VII(I), 244-252. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2022(VII-I).24
-
CHICAGO : Ahmed, Saira, Karm Shahryar Khalid, and Shaherbano Khalid. 2022. "Success Factors of E-Government and Interaction with Electronic Portal in Pakistan: A Case Study Approach." Global Social Sciences Review, VII (I): 244-252 doi: 10.31703/gssr.2022(VII-I).24
-
HARVARD : AHMED, S., KHALID, K. S. & KHALID, S. 2022. Success Factors of E-Government and Interaction with Electronic Portal in Pakistan: A Case Study Approach. Global Social Sciences Review, VII, 244-252.
-
MHRA : Ahmed, Saira, Karm Shahryar Khalid, and Shaherbano Khalid. 2022. "Success Factors of E-Government and Interaction with Electronic Portal in Pakistan: A Case Study Approach." Global Social Sciences Review, VII: 244-252
-
MLA : Ahmed, Saira, Karm Shahryar Khalid, and Shaherbano Khalid. "Success Factors of E-Government and Interaction with Electronic Portal in Pakistan: A Case Study Approach." Global Social Sciences Review, VII.I (2022): 244-252 Print.
-
OXFORD : Ahmed, Saira, Khalid, Karm Shahryar, and Khalid, Shaherbano (2022), "Success Factors of E-Government and Interaction with Electronic Portal in Pakistan: A Case Study Approach", Global Social Sciences Review, VII (I), 244-252
-
TURABIAN : Ahmed, Saira, Karm Shahryar Khalid, and Shaherbano Khalid. "Success Factors of E-Government and Interaction with Electronic Portal in Pakistan: A Case Study Approach." Global Social Sciences Review VII, no. I (2022): 244-252. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2022(VII-I).24
