- Table 1
- DemographicsVariablesN%age
- SectorPublic10452
- Private9648
- DesignationLecturer2010
- Asst Professor4924.5
- Associate Prof4522.5
- Professor8643
- Length of Service1-573.5
- 6-103316.5
- 11-155226
- 16-207437
- 20 ABOVE3417
- GenderMale16783.5
- Female3316.6
- EducationBachelor73.5
- Master6030
- Mphil12663
- Ph.D.73.5
- In Table 1 demographic characteristics of the respondents are given there are more people participated from public sector universities as compared to private i.e. N =104 which is 52% representation of respondents from public sector university. Similarly, there were 86 professors participated and 20 lecturers participated in this study. Further analysis of results revealed that there are 72 respondents participated having experience of 16-20 years while 7 people were having 1-5 years of experience. Highest number of male informants were involved in data collection in this study i.e. 167 which is 83.5% of total sample size. And there were 126 respondents having MPhil degree.
- Table 2
- SLSCSILE
- DemographicsVariablesNMeanMeanMean
- SectorPublic1043.834.0062.58
- Private963.803.972.55
- DesignationLecturer203.803.932.57
- Asst. Professor493.844.022.60
- Associate Prof.453.813.972.55
- Professor863.8163.982.56
- Length of Service1-573.823.892.59
- 6-10333.773.982.56
- 11-15523.783.992.57
- 16-20743.843.982.56
- 20 ABOVE343.863.982.57
- GenderMale1673.823.982.57
- Female333.783.92.53
- EducationBachelor73.834.012.58
- Master603.8043.972.56
- MPhil1263.823.992.56
- Ph.D.73.934.062.65
- From the analysis of results revealed mean scores of respondents on basis of demographic characteristics. It is noted that public sector employees scored higher on servant leadership as compared to private sector employees i.e. M = 3.83 while same is the case noted in cognitive style index and leadership effectiveness i.e. M = 4.006 and 2.58 respectively. Further analysis of results revealed that assistant professor scored higher on servant leadership i.e. M = 3.84 and for cognitive style index and leadership effectiveness also assistant professors score is higher M = 4.02, 2.60 respectively. But those employees having experience of more than 20 years shows more servant leadership behavior as compared to other i.e. M = 3.8 while for CSI and leadership Effectiveness almost all have the same point of view. Male respondents have more attraction towards servant leadership behavior while for leadership effectiveness both genders have same point of view but for cognitive style index males have higher score. In education PhD doctors’ behavior is more diverted towards servant leadership M = 3.93 and also same higher score is recorded for informants having doctoral degree for cognitive style index and leadership effectiveness.
- Table 3
- Correlations
- Servant leadershipCSLeadership effectivenessSL*CS
- Servant Leadership1
- Cognitive Style.666**1
- Leadership Effectiveness.777**.686**1
- SL*Cognitive Style.319**.537**.478**1
- **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
- The relationship between servant leadership styles and cognitive style is recorded r = 0.666 p<0.05 it means that there is moderate relationship between these two variables. Further analysis of results revealed that relationship between servant leadership style and leadership effectiveness is 0.777 it is strong and significant relationship. Relationship between cognitive style and leadership effectiveness is 0.686 p<0.05 so this is also moderate relationship.
- Table 4 Moderation Results
Abstract
The aim of this study is to find the moderating role of cognitive style index on servant leadership style and leadership effectiveness relationship. For this purpose, a survey was conducted on 415 teaching staff from public and private universities. A total of 200 completed questionnaires were returned and used in the analysis. Bivariate correlation and hierarchical multiple regression were used to test the hypotheses. It is concluded that cognitive style index does acts as moderator voluntary subordination, covenantal relationship and transcendent spirituality while for other it does not act as moderator. So, it means that these variables can bring change in the effectiveness of leaders while making decision to serve for society, community, employees, followers or customers.
Key Words
Servant Leadership, Cognitive Style Index, Leadership Effectiveness.
Introduction
The theory of servant leadership was first introduced by Green Leaf in 1976 in his book The Servant as Leader. This theory tells us that a servant leader first serves his/her people. The servant leader has full attention on the needs of his people in an organization and once these needs are fulfilled then it results in enhanced production levels, increases in commitment level of employees, more satisfaction from job and better leadership effectiveness (Busari, 2011). There are several models and theories of servant leadership given by different people like Page and Wong (2003), Barbuto and Wheeler (2004) and Sendjaya (2008). In this study the model of Sendjaya (2008) is adopted along with leadership effectiveness and spirituality.
Leadership Effectiveness was proposed by Busari, (2011). It has three dimensions aim, followers and groups. Yukl (2002) defined leadership effectiveness as main aim of leader: to develop goals of communication, involve others in organization’s matters, and support others i.e. followers in gaining professional and organizational goals. In addition, Nahvandi (2009) explained that point of view of a follower about one’s leaders is called leadership effectiveness. Celement and Rickard (1992) has introduced three dimensions of leadership Effectiveness i.e. tenacity, integrity and commitment. But Yukl (2002) has introduced three dimensions which are later validated by Busari (2011):goals, followers and group processes.
The human mind has two parts one depends on the left brain, called analytical, and the other deals with intuition, depending on the right brain. These were measured by cognitive style index introduced by Allinson and Hayes (1996). The way of gathering and processing the information and how he/she perceive it by one individual is called cognitive style. Most of the studies were conducted in the past like (Bass & Avolio, 1995, Avolio & Bass, 2002; Busari, 2011) on full range leadership model i.e. transformational, transactional leadership styles, laissez faire and leadership effectiveness with cognitive styles (Mughal & Busari, 2015; Busari, Mughal, Khan, Rasool & Kiyani, 2017). However, no such study has been conducted on cognitive style and leadership effectiveness by using the servant leadership style model given by Sendjaya (2008).
Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
Servant Leadership Dimensions
Voluntary Subordination
There are six dimensions given by Sendjaya (2008) one of them is voluntary subordination. In these dimensions the purpose of the leader is to be servant first i.e. to serve others not as leader. It falls under transformation leadership style. In this leader must first serve to his community, employees, society and customers rather than a leader. The study of Sendjaya (2008) got support from the previous studies of Depree (1989) and Wright (2000).
Authentic Self
This means that showing the true picture of oneself. Servant leader must show his/herself to other as he/she really are. Jesus Christ was feet of his followers and this practice is still followed by pope in churches this does not mean to show weakness but to show humility, security. These are very close to servant leadership styles. Depree (1992) explained that humility, security attributes contributed to authentic self.
Covenantal Relationship
As stated by Depree (1992) there is a strong evidence existed between contractual and covenantal relationships. Salaries, timetables, working load, fringe benefits are all obstacles in retaining the persons in organizations. But on other side when employees have common goals, objectives shared ideas and values this would result in increase in covenantal relationships in an organization.
Responsible Morality
It would raise the ethical behavior if leaders use morally ethically sound exercise of power, when these are justified then there would be no problem on both ends i.e. followers and leaders.
Transcendent Spirituality
Mitroff and Denton (1999) combined two different dimensions spirituality and leadership and emerged new paradigm as spiritual leadership but Sendjaya used this concept for religiousness, sense of mission and holistic mindset. This concept in leadership really enables the leaders to ensure that there was something in past in life which can help in understanding logic of life.
Transforming Influence
This means that leader i.e. servant leader wants to change the behavior of his followers like himself. In this style of leadership servant leader tries to motivate his followers to just show their true colors.
Cognitive Style Index
The preferred way of perceiving information and gathering that information by an individual is called cognitive style. This cognitive style was first given by Allinson and Hayes (1996) is used for decision making and problem solving. They have divided it into two parts one is analytical left brain and other is intuition right brain. Left brain people are logical, rational and used to make decision by knowing facts and figures. While intuitive people needs lot of experience, judgments, emotions and feelings for making decisions. Later on Allinson and Hayes (1996) introduced Cognitive Style index it consisting 38 items, 21 for analytical and 17 for intuition to measure whether people are analytical or intuitive.
Leadership Effectiveness
Yukl (2002) introduced three dimensions of leadership effectiveness one is goals, i.e. leaders must perform those roles which are linked with professional and organizational goals, i.e. in order to increase profit, commitment and support these are duties of leader. Second role is followers and their attitude must be towards goals of leaders, they should participate and involve themselves in organizations matters. And last one success of group i.e. leader must work for increasing the quality of group process and welfare of members, involve them in decision making.
Relationship between Servant Leadership cognitive style and Leadership Effectiveness
Relationship between cognitive style index and leadership effectiveness was first reported by Busari (2011). Analytical style is negatively related with aims and group processed while it is positively related with followers’ attitude. While intuition is positively related with aims and followers’ attitude while negatively related with group processes. While full range leadership model was positively related with aims, followers’ attitude and group process in followers’ version as well as in leaders’ version studies (Busari, 2011). In addition, cognitive style was negatively related with leadership studies in followership versions but not significantly related in leadership studies. So, this is assumed that servant leadership would also have relationship with cognitive style and leadership effectiveness.
H1: There is positive significant relationship between servant leadership, cognitive style and leadership effectiveness.
H2: There is moderating Role of Cognitive Style Index on Servant Leadership Style and Leadership Effectiveness.
Methods
Research design
A quantitative survey approach was used for this study. As this is the most used and validated way of conducting research in business administration and management sciences. In this study deductive approach was used, single method of data collection was used i.e. cross-sectional study. And total population of this study was all teaching staff from one public sector university and one private sector university. Total population was 415 teaching staff. Non probability sampling purposive sampling technique was used for taking sample. The main advantage of this sampling is that there is no need to show all information of employees who are taking part in this study. Yamane (1967) formula was used for taking sample size. SPSS 20 Version was used for analysis. Descriptive and inferential statistics was used for analysis. Cronbach alpha for servant leadership was 0.835, for cognitive style index 0.728 for leadership effectiveness 0.704 which are all acceptable.
Results
Table 1
Demographics | Variables | N | %age |
Sector | Public | 104 | 52 |
Private | 96 | 48 | |
Designation | Lecturer | 20 | 10 |
Asst Professor | 49 | 24.5 | |
Associate Prof | 45 | 22.5 | |
Professor | 86 | 43 | |
Length of Service | 1-5 | 7 | 3.5 |
6-10 | 33 | 16.5 | |
11-15 | 52 | 26 | |
16-20 | 74 | 37 | |
20 ABOVE | 34 | 17 | |
Gender | Male | 167 | 83.5 |
| Female | 33 | 16.6 |
Education | Bachelor | 7 | 3.5 |
| Master | 60 | 30 |
| Mphil | 126 | 63 |
| Ph.D. | 7 | 3.5 |
In Table 1 demographic characteristics of the respondents are given there are more people participated from public sector universities as compared to private i.e. N =104 which is 52% representation of respondents from public sector university. Similarly, there were 86 professors participated and 20 lecturers participated in this study. Further analysis of results revealed that there are 72 respondents participated having experience of 16-20 years while 7 people were having 1-5 years of experience. Highest number of male informants were involved in data collection in this study i.e. 167 which is 83.5% of total sample size. And there were 126 respondents having MPhil degree.
Table 2
|
|
| SLS | CSI | LE |
Demographics | Variables | N | Mean | Mean | Mean |
Sector | Public | 104 | 3.83 | 4.006 | 2.58 |
Private | 96 | 3.80 | 3.97 | 2.55 | |
Designation | Lecturer | 20 | 3.80 | 3.93 | 2.57 |
Asst. Professor | 49 | 3.84 | 4.02 | 2.60 | |
Associate Prof. | 45 | 3.81 | 3.97 | 2.55 | |
Professor | 86 | 3.816 | 3.98 | 2.56 | |
Length of Service | 1-5 | 7 | 3.82 | 3.89 | 2.59 |
6-10 | 33 | 3.77 | 3.98 | 2.56 | |
11-15 | 52 | 3.78 | 3.99 | 2.57 | |
16-20 | 74 | 3.84 | 3.98 | 2.56 | |
20 ABOVE | 34 | 3.86 | 3.98 | 2.57 | |
Gender | Male | 167 | 3.82 | 3.98 | 2.57 |
| Female | 33 | 3.78 | 3.9 | 2.53 |
Education | Bachelor | 7 | 3.83 | 4.01 | 2.58 |
| Master | 60 | 3.804 | 3.97 | 2.56 |
| MPhil | 126 | 3.82 | 3.99 | 2.56 |
| Ph.D. | 7 | 3.93 | 4.06 | 2.65 |
From the analysis of results revealed mean scores of respondents on basis of demographic characteristics. It is noted that public sector employees scored higher on servant leadership as compared to private sector employees i.e. M = 3.83 while same is the case noted in cognitive style index and leadership effectiveness i.e. M = 4.006 and 2.58 respectively. Further analysis of results revealed that assistant professor scored higher on servant leadership i.e. M = 3.84 and for cognitive style index and leadership effectiveness also assistant professors score is higher M = 4.02, 2.60 respectively. But those employees having experience of more than 20 years shows more servant leadership behavior as compared to other i.e. M = 3.8 while for CSI and leadership Effectiveness almost all have the same point of view. Male respondents have more attraction towards servant leadership behavior while for leadership effectiveness both genders have same point of view but for cognitive style index males have higher score. In education PhD doctors’ behavior is more diverted towards servant leadership M = 3.93 and also same higher score is recorded for informants having doctoral degree for cognitive style index and leadership effectiveness.
Table 3
Correlations | |||||
| Servant leadership | CS | Leadership effectiveness | SL*CS | |
Servant Leadership |
| 1 |
|
|
|
Cognitive Style |
| .666** | 1 |
|
|
Leadership Effectiveness |
| .777** | .686** | 1 |
|
SL*Cognitive Style |
| .319** | .537** | .478** | 1 |
|
|
|
|
| |
**. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). | |||||
The relationship between servant leadership styles and cognitive style is recorded r = 0.666 p<0.05 it means that there is moderate relationship between these two variables. Further analysis of results revealed that relationship between servant leadership style and leadership effectiveness is 0.777 it is strong and significant relationship. Relationship between cognitive style and leadership effectiveness is 0.686 p<0.05 so this is also moderate relationship.
Table 4 Moderation Results
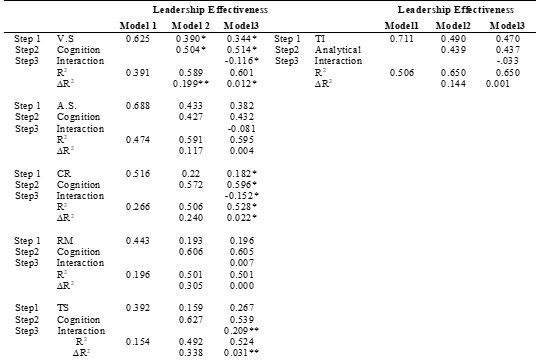
Discussion and Conclusions
Servant leadership is a very new concept in the field of management and organization settings. It is very difficult to offer yourself as servant first and to serve others but once the people follow the servant leader the results are long lasting and very effective. This concept in southern area of KP district is very new and for first time it was conducted in the universities. This study basically follows employees i.e. followers’ perspective. How the followers see their leadership in public and private universities. From the analysis it is revealed that scales of servant leadership, cognitive styles and leadership effectiveness are reliable and validated. Also, different people from different sectors participated in the study. It is concluded that there is moderate and strong relationship between servant leadership styles, cognitive style decision making or problem solving and effectiveness of leadership. Also, cognitive style does acts as moderator on relationship between servant leadership styles and leadership effectiveness. These results are in line with previous results of (Mughal & Busari, 2015; Khan, Mughal, & Khattak, 2017; Busari et al., 2017). Also found that cognitive style does acts as moderator on relationship between leadership and employees’ performance and job satisfaction and turnover intention so does as moderator on servant leadership style and leadership effectiveness. So, it is concluded that decision making is very important in enhancing the effectiveness of leaders and using specific leadership style.
References
- Aiken, L. S., & West, S. G. (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Newbury Park: Sage.
- Allinson, C.W., & Hayes, J. (1996). The cognitive style index: a measure of intuition-analysis for organizational research. Journal of Management Studies, 33 (1), 119-135, doi: 10.1111/ j.1467-6486. 1996.tb00801. x.
- Avolio, B. J. & Bass, B. M. (2002). Developing Potential across a Full Range of Leadership: Cases on transactional and transformational leadership. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Busari, A.H. (2011) Leadership effectiveness and cognitive style: a Malaysian government linked companies' (GLCS) perspectives. Thesis University of Bradford.
- Busari, A.H., Mughal, Y.H., Khan, S.N., Rasool, S., & Kiyani, A.A. (2017). Analytical cognitive style moderation on promotion and turnover intention. Journal of Management Development, 36(3), 438-464.
- De Pree, M. (1989). Leadership is an art. New York: Dell Publishing.
- Greenleaf, R.K. (1977). Servant leadership: A journey into the nature of legitimate power & greatness (25th Anniversary Ed.). Mahway, NJ: Paulist Press.
Cite this article
-
APA : Khattak, Z. Z., Abbas, S., & Kaleem, M. (2019). Servant Leadership Style and Leadership Effectiveness: The Moderating Role of the Cognitive Style Index. <i>Global Social Sciences Review, IV(II)</i>, 165-172. <a href='https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-II).22'>https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-II).22</a>
-
CHICAGO : Khattak, Zeeshan Zaib, Sammar Abbas, and Muhammad Kaleem. 2019. "Servant Leadership Style and Leadership Effectiveness: The Moderating Role of the Cognitive Style Index." <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i>, IV (II): 165-172 doi: 10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-II).22
-
HARVARD : KHATTAK, Z. Z., ABBAS, S. & KALEEM, M. 2019. Servant Leadership Style and Leadership Effectiveness: The Moderating Role of the Cognitive Style Index. <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i>, IV, 165-172.
-
MHRA : Khattak, Zeeshan Zaib, Sammar Abbas, and Muhammad Kaleem. 2019. "Servant Leadership Style and Leadership Effectiveness: The Moderating Role of the Cognitive Style Index." <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i>, IV: 165-172
-
MLA : Khattak, Zeeshan Zaib, Sammar Abbas, and Muhammad Kaleem. "Servant Leadership Style and Leadership Effectiveness: The Moderating Role of the Cognitive Style Index." <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i>, IV.II (2019): 165-172 Print.
-
OXFORD : Khattak, Zeeshan Zaib, Abbas, Sammar, and Kaleem, Muhammad (2019), "Servant Leadership Style and Leadership Effectiveness: The Moderating Role of the Cognitive Style Index", <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i>, IV (II), 165-172
-
TURABIAN : Khattak, Zeeshan Zaib, Sammar Abbas, and Muhammad Kaleem. "Servant Leadership Style and Leadership Effectiveness: The Moderating Role of the Cognitive Style Index." <i>Global Social Sciences Review</i> IV, no. II (2019): 165-172. <a href='https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-II).22'>https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2019(IV-II).22</a>
