Abstract
This research paper aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the electoral process in Sindh, shedding light on the key factors that shaped voter behaviour and influenced election outcomes. By examining the socio-political dynamics, voter demographics, campaign strategies, and the role of technology, this study offers valuable insights into the electoral symphony that unfolded during the 2018 general elections in Sindh. In the last election, PPP secured 42 seats with a vote percentage of 15.23%. The popular vote share also increased to 13.03%, although there was a slight swing of 2.29 percentage points towards a decrease. These election outcomes depict a significant shift in the political landscape of Pakistan. Imran Khan's PTI emerged as the leading party, securing the highest number of seats and a considerable popular vote share.
Key Words
Electoral Symphony, Voting Voyage, General Elections, Sindh, Pakistan
Introduction
The 2018 general elections in Sindh, Pakistan, marked a significant turning point in the political landscape of the province. This research paper aims to provide a detailed analysis of the electoral process in Sindh, focusing on the factors that influenced voter behaviour and shaped the outcomes of the elections. By examining the socio-political dynamics, voter demographics, campaign strategies, and the role of technology, this study seeks to uncover the intricacies of the electoral symphony that unfolded during the 2018 general elections in Sindh.
Sindh, one of the largest provinces in Pakistan, has a Provincial Assembly comprising 168 seats. To secure a majority in the assembly, a minimum of 85 seats is required. The 2018 general elections witnessed intense competition among various political parties vying for power and representation.
Opinion polls conducted during the election period provided valuable insights into voter preferences and anticipated voter turnout. It was observed that voter turnout during the 2018 general elections in Sindh was 48.11%, experiencing a decrease of 6.51% compared to previous elections. Understanding the factors contributing to the decrease in voter turnout is essential for assessing the democratic engagement and participation of the electorate in Sindh.
The three major political parties in Sindh during the 2018 general elections were the Pakistan Peoples Party (PPP), Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI), and Muttahida Qaumi Movement-Pakistan (MQM-P). The PPP, led by Murad Ali Shah, had previously held 91 seats with a vote share of 32.63%. The PTI, led by Imran Ismail, had only secured four seats in the previous elections, with a vote share of 6.08%. The MQM-P, led by Khawaja Izharul Hassan, had 51 seats and a vote share of 25.53%. These party leaders contested from Jamshoro-I, Karachi South-V, and Karachi Central-II, respectively.
In terms of electoral performance, the PPP emerged as the leading party in Sindh during the 2018 general elections, securing 99 seats and experiencing a seat increase of 8. The party garnered a popular vote of 3,853,081, representing a percentage of 38.44%. The PTI, with Imran Ismail at the helm, made significant gains, securing 30 seats and experiencing a seat increase of 26. The party garnered a popular vote of 1,435,813, representing a percentage of 14.47%. The MQM-P, however, experienced a decline in its performance, securing 21 seats and experiencing a seat decrease of 30. The party garnered a popular vote of 773,951, representing a percentage of 7.65%. These figures highlight the shifts in party fortunes and voter preferences during the 2018 general elections in Sindh.
The swing in popular vote share provides further insight into the changing dynamics of political support. The PPP witnessed an increase of 5.81 percentage points, indicating a growth in its popularity. The PTI saw a substantial increase of 8.39 percentage points in its vote share, reflecting the party's growing influence in Sindh. In contrast, the MQM-P experienced a significant swing of 17.88 percentage points, signalling a decrease in its electoral appeal.
The 2018 general elections in Sindh, Pakistan, served as a pivotal moment in the region's political landscape. This research paper aims to delve into the intricacies of the electoral process in Sindh, providing a comprehensive analysis of the factors that influenced voter behaviour and shaped election outcomes. By examining the socio-political dynamics, voter demographics, campaign strategies, and the role of technology, this study offers valuable insights into the electoral symphony that unfolded during the 2018 general elections in Sindh.
Elections are fundamental pillars of democracy, providing citizens with the opportunity to exercise their right to vote and shape the course of their nation's governance. Understanding the electoral process is essential for assessing the effectiveness and inclusivity of democratic systems. Sindh, as one of the largest and most populous provinces in Pakistan, holds great significance in the country's political landscape.
The political environment in Sindh is influenced by a complex interplay of historical, social, and cultural factors. The province has witnessed various political movements, ethnic tensions, and regional affiliations, all of which have contributed to the diverse political fabric of the region. Therefore, comprehending the socio-political dynamics that underpin Sindh's electoral landscape is crucial for understanding the voting behaviour and preferences of its electorate.
Demographics play a vital role in shaping electoral outcomes. Sindh is home to a diverse population with varying characteristics such as age, gender, education, income levels, and urban-rural divide. Analyzing these demographic factors provides insights into the motivations and aspirations of Sindh's voters during the 2018 general elections. Understanding the demographic composition of the electorate helps unravel the dynamics of power and representation in the province.
Campaign strategies adopted by political parties and candidates are crucial in influencing voter perceptions and electoral outcomes. Political rallies, door-to-door canvassing, social media engagement, and traditional media campaigns are integral components of electioneering efforts. Examining the campaign strategies employed in Sindh during the 2018 general elections provides valuable insights into the methods used to garner support and sway voter preferences.
Furthermore, online campaigning through social media platforms emerged as a significant tool for reaching and engaging voters (Ali, Shabbir & Ali, 2022). Evaluating the role of technology in the electoral process sheds light on its impact on voter participation, transparency, and the overall electoral experience in Sindh (Mirza & Mirza, 2020).
Analyzing the election outcomes in Sindh during the 2018 general elections offers a comprehensive understanding of the distribution of seats among political parties, the margin of victory, and any significant deviations from previous election results. By examining the factors that contributed to the success or failure of political parties and independent candidates, this research provides valuable insights into the electoral preferences of the electorate in Sindh.
Challenges faced during the 2018 general elections in Sindh and recommendations for improving the electoral process form an integral part of this research paper. Addressing issues such as voter education, electoral reforms, campaign financing, transparency, and accountability is crucial for enhancing the democratic process and ensuring the integrity of future elections in the region (Cheema & Khalid, 2019).
By analyzing the socio-political dynamics, voter demographics, campaign strategies, and the role of technology, this study provides a comprehensive exploration of the factors that shaped voter behaviour and influenced election outcomes. The findings of this research paper offer valuable insights for academics, policymakers, and practitioners, advocating for further research to strengthen democratic processes and electoral systems in Sindh and beyond (Farooqui, Latif, Khokhar, Rahim & Shabbir, 2023).
Literature Review
The following literature review provides an overview of relevant studies and scholarly works on electoral systems, voter behaviour, campaign strategies, and previous research conducted on elections in Pakistan. These sources establish a theoretical framework for analyzing the 2018 general elections in Sindh, Pakistan.
Electoral systems play a crucial role in shaping the dynamics of elections and influencing voter behaviour. Norris (2014) highlights the importance of understanding the impact of different electoral systems on representation, party competition, and voter turnout. This research emphasizes the need to consider the specific electoral system in place while analyzing the electoral process in Sindh (Ebrahim, 2019).
Voter behaviour is a multifaceted phenomenon influenced by a variety of factors. Fowler (2013) explores the psychological and social determinants of voting, emphasizing the role of personal characteristics, social context, and campaign messaging. Additionally, Berelson, Lazarsfeld, and McPhee (1954) emphasize the significance of personal motivations, party identification, and social influence in shaping voter preferences. These studies provide insights into the complexities of voter behaviour, which can be applied to understanding the electoral dynamics in Sindh (Chandio, Shabbir, Nadeemullah, 2021).
Campaign strategies are essential for political parties and candidates to effectively engage with voters. Blais and Loewen (2011) examine the impact of campaign activities on voter mobilization and electoral outcomes. Their research highlights the significance of face-to-face interactions, media campaigns, and grassroots organizing in shaping voter perceptions. In the context of Sindh, studies by Haider (2016) and Javed and Qadir (2017) provide insights into the campaign strategies employed by political parties in previous elections, shedding light on their effectiveness and implications for voter behaviour (Fowler, 2013).
Previous studies on elections in Pakistan offer valuable insights into the political landscape and electoral dynamics of the country. Khan and Afzal (2019) analyze the role of political parties, voter preferences, and electoral competitiveness in the context of Pakistan's general elections. Ahmed and Cheema (2015) investigate the impact of socioeconomic factors, ethnic divisions, and regional disparities on voting behaviour in Pakistan. These studies provide a foundation for understanding the broader political context in which the 2018 general elections in Sindh took place.
In the specific context of Sindh, research by Shah (2018) explores the role of ethnicity, patronage politics, and voter mobilization in shaping electoral outcomes in the province. This study sheds light on the socio-political dynamics specific to Sindh and their impact on the electoral process. Furthermore, Channa and Rind (2017) examine the challenges and prospects of electoral reforms in Sindh, providing insights into the need for enhancing transparency and accountability in the electoral process.
Methodology
This research paper employs a mixed-methods approach to comprehensively analyze the 2018 general elections in Sindh, Pakistan. The methodology includes both quantitative and qualitative techniques to capture a holistic understanding of the electoral process, voter behaviour, and campaign strategies.
Data Collection: Qualitative data is obtained through interviews with key stakeholders, including political party representatives, election officials, and voters. These interviews provide insights into campaign strategies, perceptions, and experiences during the election period.
Data Analysis: The qualitative data from interviews is transcribed, coded, and thematically analyzed. The analysis identifies recurring themes, patterns, and insights related to voter behaviour, campaign strategies, and other pertinent factors.
Election Outcomes
The 2018 general elections in Sindh witnessed significant changes in the political landscape, with several parties vying for the 168 seats in the Provincial Assembly. This section delves into the election outcomes, highlighting seat distribution, popular vote shares, and the overall impact on party dynamics in Sindh (Mumtaz & Khan, 2019).
The Provincial Assembly of Sindh consists of 168 seats, with 85 seats needed for a majority. The Pakistan People’s Party (PPP), led by Murad Ali Shah, emerged as the dominant party in the province. In the previous election, the PPP had secured 91 seats, but in the 2018 elections, they managed to increase their tally, winning 99 seats. This increase of 8 seats demonstrated the party's continued stronghold in Sindh.
The Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI), led by Imran Ismail, made significant inroads in Sindh, particularly in urban areas. In the previous election, the PTI had only secured 4 seats, but in the 2018 elections, they experienced a remarkable surge, winning 30 seats. This increase of 26 seats marked a significant shift in party dynamics and indicated a growing popularity of the PTI in Sindh (Shabbir, Ansari et. al, 2021).
The Muttahida Qaumi Movement-Pakistan (MQM-P), led by Khawaja Izharul Hassan, faced a decline in its electoral performance. In the previous election, the MQM-P had secured 51 seats, but in the 2018 elections, they experienced a significant setback, winning only 21 seats. This decrease of 30 seats reflected a decline in the party's influence in Sindh Shabbir, Chandio, Uddin, & Ali, 2021).
The popular vote shares also provide insights into the election outcomes. The PPP secured the highest popular vote share in Sindh, with 38.44% of the votes. The PTI, with its increased seat tally, garnered a popular vote share of 14.47%. The MQM-P, despite the decline in seats, managed to secure a popular vote share of 7.65%.
The election outcomes in Sindh had significant implications for party dynamics and governance in the province. The increased seat tally for the PPP consolidated their position as the ruling party, allowing them to form the government in Sindh. The PTI's improved performance established them as a formidable opposition and signalled a shift in urban voter preferences. The MQM-P's decreased seat tally challenged their previous dominance and required the party to reassess its strategies (Riaz & Khan, 2021).
Election outcomes in Sindh showcased a mix of continuity and change. While the PPP maintained its stronghold, the PTI's surge and the decline of the MQM-P reshaped the political landscape in the province. These outcomes set the stage for the governance and political dynamics in Sindh in the aftermath of the 2018 general elections.
Figure
Map of Sindh Showing Assembly Constituencies and Winning Parties
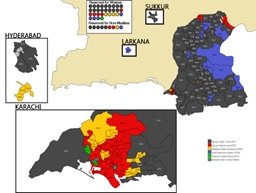
Socio-Political Dynamics
Sindh, a province of Pakistan, has a unique socio-political landscape that influences the voting patterns of its residents. Understanding the socio-political dynamics is crucial for analyzing the 2018 general elections in Sindh. Historical context, regional affiliations, and ethnic dynamics played significant roles in shaping the candidate selection process and voter preferences (Kausar, 2017).
Sindh has a rich historical background, with a legacy of influential political families and dynasties. These historical ties, along with patronage politics, have contributed to a complex web of political alliances and rivalries. The presence of influential political families, such as the Bhuttos and the Sharifs, has traditionally shaped the political landscape in Sindh.
Ethnic dynamics also play a crucial role in Sindh's politics. The province is home to diverse ethnic communities, including Sindhis, Mohajirs, Punjabis, and Pashtuns. The Mohajir community, primarily concentrated in urban areas like Karachi, has historically been associated with the Muttahida Qaumi Movement-Pakistan (MQM-P). The Sindhi community, on the other hand, has been aligned with the Pakistan People's Party (PPP). These ethnic affiliations, combined with issues of identity and resource distribution, have influenced candidate selection and voter preferences in Sindh (Tahir, Bhatti & Haider, 2019).
Voter Demographics
An analysis of voter demographics provides insights into the characteristics of the electorate during the 2018 general elections in Sindh. Factors such as age, gender, education, income, and the urban-rural divide play a significant role in shaping voter turnout and party preferences (Shah, Khan & Jan, 2018).
Age demographics reveal the level of political engagement among different age groups. Younger voters, with their growing influence and aspirations for change, may have different political priorities compared to older generations. Gender dynamics also play a crucial role, with variations in political participation and preferences among male and female voters (Shahbaz & Farooq, 2019).
Educational attainment and income levels are key determinants of political awareness and voter behaviour. Highly educated individuals may exhibit different voting patterns compared to those with limited education. Similarly, income disparities can influence voter preferences, as economic considerations often shape political choices (Shakoor, Shabbir, & Ansari, 2021).
The urban-rural divide in Sindh also impacts voting patterns. Urban areas, such as Karachi and Hyderabad, present distinct challenges and opportunities compared to rural areas. Urban voters may have different concerns related to infrastructure, public services, and employment, which can shape their voting decisions (Shabbir, Nadeemullah, & Chandio, 2022).
Campaign Strategies
The campaign strategies employed by political parties and candidates during the 2018 general elections played a crucial role in shaping voter perceptions and electoral outcomes in Sindh. Political rallies, door-to-door campaigning, social media, and traditional media all played a part in influencing voter behaviour (Shabbir, Ansari, Abbasi, & Memon, 2018).
Large-scale political rallies have traditionally been a prominent feature of election campaigns in Sindh. These rallies serve as a platform for parties to showcase their strength, convey their messages, and mobilize supporters. The size and enthusiasm of rally attendees can generate momentum and influence voter perceptions (Khan & Arshad, 2020).
Door-to-door campaigning allows candidates to connect directly with voters, addressing their concerns and seeking their support. Personal interactions during such campaigns can be influential, as they provide an opportunity for candidates to establish rapport and build trust with voters (Shabbir, 2021).
The rise of social media has revolutionized election campaigns, enabling political parties and candidates to reach a wider audience and engage with voters in new ways. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram provide avenues for sharing campaign messages, mobilizing supporters, and countering opponents. Social media campaigns allow for more targeted messaging and interaction with specific voter segments (Shabbir, Abro, & Khan, 2017).
Traditional media, including television, radio, and newspapers, also play a significant role in shaping voter perceptions. Political advertisements, interviews, and news coverage can influence voter opinions and contribute to the overall narrative surrounding the elections Shabbir, Ali, Uddin, Wazir & Gopang, M. A., n.d)
Challenges and Recommendations
Challenges: Challenges: The 2018 general elections in Sindh were not without challenges. This section highlights some of the key challenges encountered during the electoral process and provides recommendations for addressing these challenges in future elections.
i. Voter Turnout: One of the primary challenges was the relatively low voter turnout of 48.11% in Sindh, which indicated a decrease of 6.51% compared to previous elections. Encouraging greater participation and engagement among voters is essential for a healthy democratic process. Efforts should be made to raise awareness, educate voters about their rights and responsibilities, and address any barriers that may hinder voter turnout.
ii. Electoral Violence and Security: Electoral violence and security concerns have been persistent challenges in the electoral process. During the 2018 elections, incidents of violence were reported in certain constituencies, which may have discouraged voter participation and compromised the integrity of the process. Strengthening security measures, ensuring the safety of voters and election officials, and holding accountable those responsible for electoral violence are crucial steps to address this challenge.
iii. Fair and Transparent Electoral Processes: Ensuring fair and transparent electoral processes is essential for building trust in the electoral system. The effective functioning of electoral institutions, such as the Election Commission of Pakistan (ECP), is vital in this regard. Continuous efforts should be made to enhance the transparency of voter registration, candidate selection, and result tabulation processes. The ECP should be empowered with adequate resources and authority to oversee the electoral process and address any grievances or irregularities.
iv. Political Party Financing: The issue of political party financing and its impact on the electoral process is another significant challenge. Transparent and accountable systems for campaign financing should be put in place to prevent undue influence, corruption, and the use of unaccounted-for resources during elections. Stricter regulations and effective monitoring mechanisms can help mitigate this challenge and promote a level playing field for all political parties.
v. Media Ethics and Misinformation: The role of media in shaping public opinion and influencing electoral outcomes cannot be underestimated. However, the spread of misinformation and biased reporting pose challenges to fair and objective coverage of elections. Ensuring media ethics, promoting responsible journalism, and raising awareness among voters about media literacy are essential steps to address this challenge.
Recommendations
To overcome the challenges encountered during the 2018 general elections in Sindh and strengthen the electoral process, the following recommendations are proposed:
i. Voter Education and Awareness: Launch comprehensive voter education campaigns to increase awareness about voting rights, the importance of participation, and the electoral process. Targeted efforts should be made to engage youth, women, and marginalized communities.
ii. Enhanced Security Measures: Strengthen security arrangements to ensure the safety of voters, candidates, and election officials. Collaboration between law enforcement agencies, political parties, and community leaders can help maintain a peaceful electoral environment.
iii. Strengthening Electoral Institutions: Provide necessary resources and support to electoral institutions, such as the ECP, to enhance their capacity and effectiveness. Strengthen the autonomy and authority of these institutions to maintain the integrity and transparency of the electoral process.
iv. Political Finance Reforms: Implement comprehensive reforms in political party financing to promote transparency, accountability, and a level playing field. Introduce stricter regulations, disclosure requirements, and independent auditing of campaign finances.
v. Media Literacy and Regulation: Promote media literacy programs to equip voters with the skills to critically evaluate information and combat misinformation. Strengthen media regulations to ensure fair and unbiased coverage of elections, and hold media outlets accountable for ethical violations.
vi. Civic Engagement and Participation: Encourage civic engagement through community-based initiatives, public forums, and platforms for dialogue between voters and candidates. Foster a culture of active citizenship to promote greater participation in the electoral process.
Conclusion
The 2018 general elections in Sindh marked a significant chapter in the province's political landscape. The socio-political dynamics, voter demographics, campaign strategies, and the role of technology all played critical roles in shaping the electoral process and outcomes. Through an insightful exploration of these factors, this research paper has provided a comprehensive understanding of Sindh's voting voyage during the 2018 elections.
The election outcomes highlighted the dominance of the Pakistan Peoples Party (PPP), the remarkable surge of the Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI), and the decline of the Muttahida Qaumi Movement-Pakistan (MQM-P). These outcomes have reshaped the party dynamics in Sindh, paving the way for a new political landscape and setting the stage for governance in the province.
However, the elections were not without challenges. Low voter turnout, electoral violence, concerns about fair and transparent processes, political party financing, and the spread of misinformation all posed significant obstacles. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure a healthy and vibrant democratic process in Sindh.
To overcome these challenges, several recommendations have been proposed. These include voter education and awareness campaigns, enhanced security measures, strengthening electoral institutions, implementing political finance reforms, promoting media literacy, and fostering civic engagement and participation. By implementing these recommendations, the electoral process in Sindh can be strengthened, ensuring a more inclusive, transparent, and participatory democracy.
As Sindh prepares for future elections, it is imperative to build upon the lessons learned from the 2018 general elections. By continuously striving to enhance voter engagement, ensure the integrity of the electoral process, and promote an informed and empowered electorate, Sindh can strengthen its democratic foundations and contribute to the overall democratic development of Pakistan.
The electoral symphony that unfolded during the 2018 general elections in Sindh serves as a reminder of the dynamic nature of politics and the power of the people's voice. By continuously striving for fairness, inclusivity, and transparency, Sindh can embark on a journey towards a stronger and more vibrant democracy, where the electoral process truly reflects the will and aspirations of its diverse population.
References
- Ali, A., Shabbir, T., & Ali, W. (2022). A Literature Review on Public Leadership in Organizations. International Journal of Educational Administration, Management, and Leadership, 1–10.
- Berelson, B. R., Lazarsfeld, P. F., & McPhee, W. N. (1954). Voting: A Study of Opinion Formation in a Presidential Campaign. University of Chicago Press.
- Blais, A., & Loewen, P. J. (2011). Comparing Voters, Parties, and Candidates: Continuity and Change in Canadian Elections. UBC Press.
- Chandio, A. S., Shabbir, T., Nadeemullah, M., & Ali, A. (2021). Genesis of Federalism in Pakistan: A Historical Analysis. International Journal of Educational Administration, Management, and Leadership, 91–102.
- Cheema, M. A., & Khalid, M. (2019). Determinants of Voter Turnout in Pakistan: A District-Level Analysis. The Pakistan Development Review, 58(3), 345-366.
- Ebrahim, Z. (2019). Electoral Manipulation and Political Stability: Evidence from Pakistan. World Development, 117, 222-235.
- Farooqui, D. Y. S., Author), D. M. L. (Corresponding, Khokhar, A. S., Rahim, A., & Shabbir, D. T. (2023). Harnessing Interactive Media For Transformative Education In Pakistan: A Case Study Of Virtual Reality Integration. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 7(6), 165–179.
- Fowler, J. H. (2013). Elections and the Mobilization of Popular Support. Annual Review of Political Science, 16, 285-302.
- Kausar, S. (2017). Electoral Behavior in Pakistan: An Analysis of Provincial Assembly Elections in Punjab. Journal of Political Studies, 24(1), 53-68.
- Khan, A. R., & Arshad, S. (2020). Dynamics of Ethnic Voting in Pakistan: A Case Study of Sindh Province. Journal of Political Science and International Relations, 13(1), 34-47.
- Mirza, M. S., & Mirza, M. A. (2020). A Comprehensive Analysis of the Influence of Political Dynasties on Pakistani Politics. South Asian Studies, 35(1), 157-169.
- Mumtaz, Z., & Khan, M. K. (2019). Understanding the Relationship between Voter Turnout and Electoral Systems in Pakistan: An Empirical Analysis. Pakistan Vision, 20(2), 185-204.
Cite this article
-
APA : Rahim, A., & Nadeemullah, M. (2023). The Electoral Symphony: Unveiling Sindh's Voting Voyage (An Insightful Exploration of the 2018 General Elections). Global Social Sciences Review, VIII(II), 648-656. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2023(VIII-II).57
-
CHICAGO : Rahim, Abdul, and Muhammad Nadeemullah. 2023. "The Electoral Symphony: Unveiling Sindh's Voting Voyage (An Insightful Exploration of the 2018 General Elections)." Global Social Sciences Review, VIII (II): 648-656 doi: 10.31703/gssr.2023(VIII-II).57
-
HARVARD : RAHIM, A. & NADEEMULLAH, M. 2023. The Electoral Symphony: Unveiling Sindh's Voting Voyage (An Insightful Exploration of the 2018 General Elections). Global Social Sciences Review, VIII, 648-656.
-
MHRA : Rahim, Abdul, and Muhammad Nadeemullah. 2023. "The Electoral Symphony: Unveiling Sindh's Voting Voyage (An Insightful Exploration of the 2018 General Elections)." Global Social Sciences Review, VIII: 648-656
-
MLA : Rahim, Abdul, and Muhammad Nadeemullah. "The Electoral Symphony: Unveiling Sindh's Voting Voyage (An Insightful Exploration of the 2018 General Elections)." Global Social Sciences Review, VIII.II (2023): 648-656 Print.
-
OXFORD : Rahim, Abdul and Nadeemullah, Muhammad (2023), "The Electoral Symphony: Unveiling Sindh's Voting Voyage (An Insightful Exploration of the 2018 General Elections)", Global Social Sciences Review, VIII (II), 648-656
-
TURABIAN : Rahim, Abdul, and Muhammad Nadeemullah. "The Electoral Symphony: Unveiling Sindh's Voting Voyage (An Insightful Exploration of the 2018 General Elections)." Global Social Sciences Review VIII, no. II (2023): 648-656. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2023(VIII-II).57
